Case series: Cervical far-lateral and combined cervical far lateral/foraminal intervertebral disk extrusions in 10 dogs
- PMID: 39606656
- PMCID: PMC11600107
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1465182
Case series: Cervical far-lateral and combined cervical far lateral/foraminal intervertebral disk extrusions in 10 dogs
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Case series: cervical far-lateral and combined cervical far lateral/foraminal intervertebral disk extrusions in 10 dogs.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Apr 17;12:1609269. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1609269. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40313634 Free PMC article.
Abstract
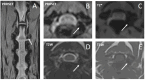
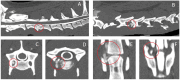
Far-lateral intervertebral disk extrusions (IVDEs) have been reported infrequently in dogs in veterinary literature, mostly affecting the caudal lumbar intervertebral disks. We describe the clinical findings, computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings, treatment, and outcome in 10 dogs with cervical far-lateral IVDEs. Patient databases of 3 small animal hospitals and 1 veterinary teleradiology service were retrospectively searched for patients in which imaging studies (CT or MRI) identified the presence of intervertebral disk material outside the limits of the intervertebral foramen. Presenting clinical signs included: episodic signs of cervical pain (6/10, 30%), persistent signs of cervical pain (3/10, 50%), nerve root signature or lameness (5/10, 50%), and abnormal cervical posture only (excluding nerve root signature) (1/10, 10%). Affected IVD spaces (for 11 IVDEs in 10 dogs) included: C3-4 (6/11, 55%), C5-6 (3/11, 27%), and C2-3 (2/11, 18%). Nerve root signature was not reported for C2-3 IVDEs. All cases were managed medically (without surgery). The top 3 used medications were gabapentinoids (10/10, 100%), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (10/10, 100%), and paracetamol (3/10, 30%). Median treatment duration was 25 days (range 10-84). Short-term outcome (<3 months) was recorded in 9/10 (90%) cases. Resolution of clinical signs was reported in 7/9 (78%) cases. Long-term follow-up was available for 6/10 (60%) cases (median 11.5 months, range 5.5-30 months); 5/6 (83%) showed resolution of clinical signs. Recurrence of clinical signs was reported in 1 case (9 months later), managed medically again, with successful outcome. In conclusion, cervical far-lateral disk extrusions are a rare clinical entity in dogs, but can result in severe, persistent or episodic, pain. Medical management is associated with a positive short- and long-term outcome in most cases.
Keywords: chondrodystrophic; herniation; hyperesthesia; nerve root signature; pain.
Copyright © 2024 Santifort, Gomes, Ruggeri, Alcoverro, Tauro, Lichtenauer, Van Soens, Garosi, Carrera, Bergknut, Farre Marine and Luján Feliu-Pascual.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Spitzbarth I, Moore SA, Stein VM, Levine JM, Kühl B, Gerhauser I, et al. Canine spinal cord injury consortium (CANSORT-SCI). Current insights into the pathology of canine intervertebral disc extrusion-induced spinal cord injury. Front Vet Sci. (2020) 7:595796. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.595796, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

