Ovine conceptuses express phospholipase inhibitory genes on days 14-15 of pregnancy, interacting with IFNT pathways
- PMID: 39606929
- PMCID: PMC11935640
- DOI: 10.1530/REP-24-0286
Ovine conceptuses express phospholipase inhibitory genes on days 14-15 of pregnancy, interacting with IFNT pathways
Abstract
In brief: Ovine conceptuses highly express phospholipase inhibitory genes just before the conceptus attachment period. Phospholipase inhibitors could synergistically work with the interferon pathway on the endometrium.
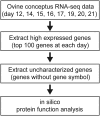
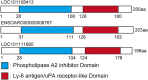
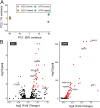
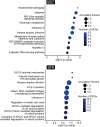
Abstract: In mammals, various molecules are involved in the biochemical interaction between the conceptus and endometrium for pregnancy recognition and establishment. In ruminants, interferon tau (IFNT) is the pregnancy recognition factor; however, IFNT alone does not explain corpus luteum maintenance. Although data on factors expressed during implantation have been accumulated, we hypothesized that the conceptus produces additional uncharacterized molecules during the period of conceptus attachment. This study aimed to identify new conceptus secretory proteins involved in the biochemical interaction between the conceptus and endometrium in sheep. We analyzed RNA-sequence data of ovine conceptuses from pregnant animals on days 12, 14, 15, 16, 17, 19, 20 and 21. To identify novel secretory proteins, we focused on highly expressed but uncharacterized genes and performed in silico protein function analysis, identifying genes encoding phospholipase inhibitory proteins expressed on days 14 and 15. Recombinant proteins from these genes were produced, and the effects on cultured bovine endometrial epithelial cells (EECs) and stromal cells (STRs) were analyzed by RNA-sequence analysis. Differentially expressed gene (DEG) analysis demonstrated that the recombinant protein treatment upregulated 31 genes and downregulated 4 genes in EECs; it also upregulated 398 genes and downregulated 66 genes in STRs, including implantation-related genes, such as ISG15, OAS1X, OAS1Y, PARP9, PARP14, MX1 and PTGS2. Gene set enrichment analysis revealed that DEGs were enriched in several implantation-related pathways, including ISG15 antivirus mechanisms. These results suggest that, in addition to numerous characterized molecules, phospholipase inhibitory protein is a new candidate molecule in enabling biochemical communication between the conceptus and endometrium.
Keywords: conceptus; phospholipase inhibitor; sheep; uncharacterized genes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the work.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

