Uncontrolled Cholesterol in Individuals with Severe Hypercholesterolemia in a Health Evaluation Program in Brazil
- PMID: 39607222
- PMCID: PMC11634292
- DOI: 10.36660/abc.20240116
Uncontrolled Cholesterol in Individuals with Severe Hypercholesterolemia in a Health Evaluation Program in Brazil
Abstract
Background: Individuals with severe hypercholesterolemia (SH) are considered at high atherosclerosis risk and should be intensively treated with lipid-lowering drugs aiming for an LDL-C reduction of≥50% and a goal of <70 mg/dL.
Objectives: This study aimed to evaluate cholesterol control in individuals with SH (LDL-C ≥ 190 mg/dL or 160-189 mg/dL using lipid-lowering drugs) followed in a health evaluation program.
Methods: 55,000 individuals were evaluated, of which 2,214 (4%) had SH, and 1,016 (45.8%) had repeated assessments. Achievement of recommended LDL-C goals was the primary study endpoint. A p-value < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results: Mean age (± SD) was 44.9±8.8 years, 84.2% were men, and 0.5% reported previous myocardial infarction. Mean LDL-C was 203.0±22.0 mg/dL, and although 62.5% referred dyslipidemia, only 19% were using lipid-lowering drugs (5.9% in cases with LDL-C ≥ 190 mg/dL). During a 4.1±2.8-year follow-up, use of lipid-lowering drugs increased from 18.1% to 48.4% (p<0.00001), 5.9% to 45.4% in those with LDL-C ≥ 190 mg/dL (p< 0.00001) though 31% of cases with LDL-C 160-189 mg/dL stopped taking medications. Overall, there was a mean 26.7% reduction in LDL-C (p<0.0001), and LDL-C reductions ≥50% were attained in 19.2%, 19.1%, and 19.7 % of all individuals, and in those with LDL-C > 190 mg/dL and 160-189 mg/dL respectively. Only 3.1% reached LDL-C < 70 mg/dL (2.7% in those with LDL-C ≥ 190 and 5.3% in those with 160-189 mg/dL).
Conclusions: A serious gap was found between treatment recommendations and reality in individuals at high atherosclerosis risk due to SH.
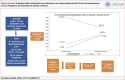
Figura Central: Colesterol Não Controlado em Indivíduos com Hipercolesterolemia Grave Acompanhados em um Programa de Avaliação da Saúde no Brasil Ausência de controle dos níveis de colesterol na hipercolesterolemia grave.
Plain language summary
Central Illustration : Uncontrolled Cholesterol in Individuals with Severe Hypercholesterolemia in a Health Evaluation Program in Brazil Lack of cholesterol control in severe hypercholesterolemia.
Conflict of interest statement
Fernando Yue Cesena - Sup e educacional da Novo-Nordisk.
Otavio Berwanger - recebeu subsídios da AstraZeneca, Amgen, Servier, Bristol Myers Squibb, Bayer, Novartis, Pfizer e Boehringer Ingelheim.
Figures







References
-
- Grundy SM, Stone NJ, Bailey AL, Beam C, Birtcher KK, Blumenthal RS, et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73(24):3168–3209. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.11.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abdullah SM, Defina LF, Leonard D, Barlow CE, Radford NB, Willis BL, et al. Long-term Association of Low-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol with Cardiovascular Mortality in Individuals at Low 10-Year Risk of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation. 2018;138(21):2315–2325. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.034273. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

