A deep learning approach for automated scoring of the Rey-Osterrieth complex figure
- PMID: 39607424
- PMCID: PMC11604216
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.96017
A deep learning approach for automated scoring of the Rey-Osterrieth complex figure
Abstract
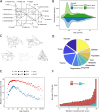
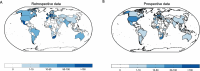
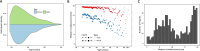
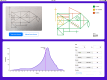
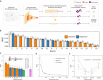
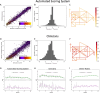
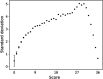
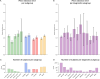
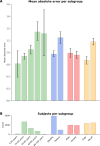
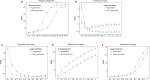
Memory deficits are a hallmark of many different neurological and psychiatric conditions. The Rey-Osterrieth complex figure (ROCF) is the state-of-the-art assessment tool for neuropsychologists across the globe to assess the degree of non-verbal visual memory deterioration. To obtain a score, a trained clinician inspects a patient's ROCF drawing and quantifies deviations from the original figure. This manual procedure is time-consuming, slow and scores vary depending on the clinician's experience, motivation, and tiredness. Here, we leverage novel deep learning architectures to automatize the rating of memory deficits. For this, we collected more than 20k hand-drawn ROCF drawings from patients with various neurological and psychiatric disorders as well as healthy participants. Unbiased ground truth ROCF scores were obtained from crowdsourced human intelligence. This dataset was used to train and evaluate a multihead convolutional neural network. The model performs highly unbiased as it yielded predictions very close to the ground truth and the error was similarly distributed around zero. The neural network outperforms both online raters and clinicians. The scoring system can reliably identify and accurately score individual figure elements in previously unseen ROCF drawings, which facilitates explainability of the AI-scoring system. To ensure generalizability and clinical utility, the model performance was successfully replicated in a large independent prospective validation study that was pre-registered prior to data collection. Our AI-powered scoring system provides healthcare institutions worldwide with a digital tool to assess objectively, reliably, and time-efficiently the performance in the ROCF test from hand-drawn images.
Keywords: ROCF; Rey–Osterrieth complex figure; crowdsourced human intelligence; deep learning; memory deficit; neuropsychology; neuroscience; non-verbal visual memory; none.
© 2024, Langer et al.
Conflict of interest statement
NL, MW, BH, DS, LW, AP, JH, SM, CS, MT, JL, DR, FS, QZ, RL, FW, OJ, PB, TZ, RL, CZ No competing interests declared
Figures



Update of
- doi: 10.1101/2022.06.15.496291
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.96017.1
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.96017.2
References
-
- Berry DTR, Allen RS, Schmitt FA. Rey-Osterrieth complex figure: Psychometric characteristics in a geriatric sample. Clinical Neuropsychologist. 1991;5:143–153. doi: 10.1080/13854049108403298. - DOI
-
- Bin Nazar H, Moetesum M, Ehsan S, Siddiqi I, Khurshid K, Vincent N, McDonald-Maier KD. Classification of Graphomotor Impressions Using Convolutional Neural Networks: An Application to Automated Neuro-Psychological Screening Tests. 2017 14th IAPR International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition (ICDAR; 2017. - DOI
-
- Buolamwini J, Gebru T. Gender Shades: Intersectional Accuracy Disparities in Commercial Gender Classification. Proceedings of the 1st Conference on Fairness, Accountability and Transparency.2018.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

