CD spectra reveal the state of G-quadruplexes and i-motifs in repeated and other DNA sequences
- PMID: 39608571
- PMCID: PMC11699388
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpr.2024.100187
CD spectra reveal the state of G-quadruplexes and i-motifs in repeated and other DNA sequences
Abstract
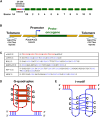
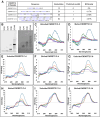
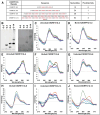
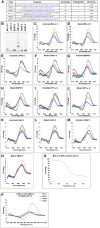
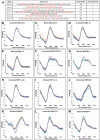
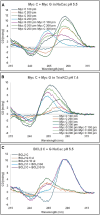
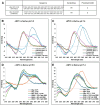
The B-DNA of the genome contains numerous sequences that can form various noncanonical structures including G-quadruplex (G4), formed by two or more stacks of four guanine residues in a plane, and intercalating motif (i-motif [iM]) formed by alternately arranged C-C+ pairs. One of the easy yet sensitive methods to study G4s and iMs is circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy, which generates characteristic G4 and iM peaks. We have analyzed and compared the effects of various environmental factors including pH, buffer composition, temperature, flanking sequences, complimentary DNA strands, and single-stranded DNA binding protein (SSB) on the CD patterns of G4s and iMs generated by two groups of DNA molecules, one containing tandem repeats of GGGGCC and CCCCGG from the C9ORF72 gene associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia, and the second containing polyG/polyC clusters from oncogene promoter-proximal regions without such tandem repeats. Changes in pH caused drastic changes in CCCCGG-iM and GGGGCC-G4 and the changes were dependent on repeat numbers and G-C basepairing. In contrast, with the DNA sequences from the promoter-proximal regions of oncogenes, iMs disassembled upon pH changes with the peak slowly shifting to lower wavelength but the G4s did not show significant change. Complementary DNA strands and flanking DNA sequences also regulate G4 and iM formation. The SSB disassembled both G4s and iMs formed by almost all sequences suggesting an in vivo role for SSBs in the disassembly of G4s and iMs during DNA replication and other DNA transactions.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The author declares no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Kaushik M., Kaushik S., et al. Kukreti S. Structural diversity and specific recognition of four stranded G-quadruplex DNA. Curr. Mol. Med. 2011;11:744–769. - PubMed
-
- Ortiz de Luzuriaga I., Lopez X., Gil A. Learning to Model G-Quadruplexes: Current Methods and Perspectives. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2021;50:209–243. - PubMed
-
- Alba J.J., Sadurní A., Gargallo R. Nucleic Acid i-Motif Structures in Analytical Chemistry. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2016;46:443–454. - PubMed
-
- Chambers V.S., Marsico G., et al. Balasubramanian S. High-throughput sequencing of DNA G-quadruplex structures in the human genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015;33:877–881. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

