Degradation of PARP1 by MARCHF3 in tumor cells triggers cCAS-STING activation in dendritic cells to regulate antitumor immunity in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 39608977
- PMCID: PMC11605840
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2024-010157
Degradation of PARP1 by MARCHF3 in tumor cells triggers cCAS-STING activation in dendritic cells to regulate antitumor immunity in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) significantly limits the efficacy of immunotherapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the mechanisms underlying immunotherapy resistance remain poorly understood. Our aim was to clarify the role of membrane-associated ring-CH-type finger 3 (MARCHF3) in HCC within the framework of anti-programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) therapy.
Methods: MARCHF3 was identified in the transcriptomic profiles of HCC tumors exhibiting different responses to ICIs. In humans, the correlation between MARCHF3 expression and the tumor microenvironment (TME) was assessed via multiplex immunohistochemistry. In addition, MARCHF3 expression in tumor cells and immune cell infiltration were assessed by flow cytometry.
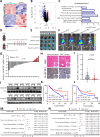
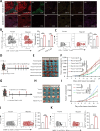
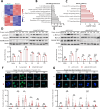
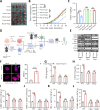
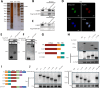
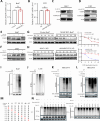
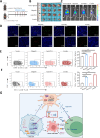
Results: MARCHF3 was significantly upregulated in tumors from patients who responded to ICIs. Increased MARCHF3 expression in HCC cells promoted dendritic cell (DC) maturation and stimulated CD8+ T-cell activation, thereby augmenting tumor control. Mechanistically, we identified MARCHF3 as a pivotal regulator of the DNA damage response. It directly interacted with Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase 1 (PARP1) via K48-linked ubiquitination, leading to PARP1 degradation. This process promoted the release of double-strand DNA and activated cCAS-STING in DCs, thereby initiating DC-mediated antigen cross-presentation and CD8+ T-cell activation. Additionally, ATF4 transcriptionally regulated MARCHF3 expression. Notably, the PARP1 inhibitor olaparib augmented the efficacy of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in both subcutaneous and orthotopic HCC mouse models.
Conclusions: MARCHF3 has emerged as a pivotal regulator of the immune landscape in the HCC TME and is a potent predictive biomarker for HCC. Combining interventions targeting the DNA damage response with ICIs is a promising treatment strategy for HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular Carcinoma; Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor; Immunotherapy; Tumor microenvironment - TME.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: No, there are no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
