MS-DIAL 5 multimodal mass spectrometry data mining unveils lipidome complexities
- PMID: 39609386
- PMCID: PMC11605090
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-54137-w
MS-DIAL 5 multimodal mass spectrometry data mining unveils lipidome complexities
Abstract
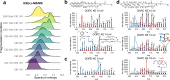
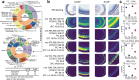
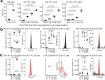
Lipidomics and metabolomics communities comprise various informatics tools; however, software programs handling multimodal mass spectrometry (MS) data with structural annotations guided by the Lipidomics Standards Initiative are limited. Here, we provide MS-DIAL 5 for in-depth lipidome structural elucidation through electron-activated dissociation (EAD)-based tandem MS and determining their molecular localization through MS imaging (MSI) data using a species/tissue-specific lipidome database containing the predicted collision-cross section values. With the optimized EAD settings using 14 eV kinetic energy, the program correctly delineated lipid structures for 96.4% of authentic standards, among which 78.0% had the sn-, OH-, and/or C = C positions correctly assigned at concentrations exceeding 1 μM. We showcased our workflow by annotating the sn- and double-bond positions of eye-specific phosphatidylcholines containing very-long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (VLC-PUFAs), characterized as PC n-3-VLC-PUFA/FA. Using MSI data from the eye and n-3-VLC-PUFA-supplemented HeLa cells, we identified glycerol 3-phosphate acyltransferase as an enzyme candidate responsible for incorporating n-3 VLC-PUFAs into the sn1 position of phospholipids in mammalian cells, which was confirmed using EAD-MS/MS and recombinant proteins in a cell-free system. Therefore, the MS-DIAL 5 environment, combined with optimized MS data acquisition methods, facilitates a better understanding of lipid structures and their localization, offering insights into lipid biology.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: U.T. is an application specialist in ABSciex, Japan. K.T. and S.T. are the research scientists in AGC Inc., Japan. M.O. and Hidenori T. are research scientists at SHIMADZU CORPORATION, Japan. All the other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Rakusanova, S., Fiehn, O. & Cajka, T. Toward building mass spectrometry-based metabolomics and lipidomics atlases for biological and clinical research. Trac-Trend Anal. Chem.158, 116825 (2023).
-
- Shi, H. X. et al. Visible-Light Paterno-Buchi Reaction for Lipidomic Profiling at Detailed Structure Levels. Anal. Chem.95, 5117–5125 (2023). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 21K18216, 24K02011, 24H00043, 24H00392, 24K21269/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- 21wm0325036h0001, JP15dm0207001/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED)
- JPMJER2101/MEXT | JST | Exploratory Research for Advanced Technology (ERATO)
- JPMJND2305/MEXT | JST | National Bioscience Database Center (NBDC)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

