The dual GLP-1/glucagon receptor agonist G49 mimics bariatric surgery effects by inducing metabolic rewiring and inter-organ crosstalk
- PMID: 39609390
- PMCID: PMC11605122
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-54080-w
The dual GLP-1/glucagon receptor agonist G49 mimics bariatric surgery effects by inducing metabolic rewiring and inter-organ crosstalk
Abstract
Bariatric surgery is effective for the treatment and remission of obesity and type 2 diabetes, but pharmacological approaches which exert similar metabolic adaptations are needed to avoid post-surgical complications. Here we show how G49, an oxyntomodulin (OXM) analog and dual glucagon/glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GCGR/GLP-1R) agonist, triggers an inter-organ crosstalk between adipose tissue, pancreas, and liver which is initiated by a rapid release of free fatty acids (FFAs) by white adipose tissue (WAT) in a GCGR-dependent manner. This interactome leads to elevations in adiponectin and fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), causing WAT beiging, brown adipose tissue (BAT) activation, increased energy expenditure (EE) and weight loss. Elevation of OXM, under basal and postprandial conditions, and similar metabolic adaptations after G49 treatment were found in plasma from patients with obesity early after metabolic bariatric surgery. These results identify G49 as a potential pharmacological alternative sharing with bariatric surgery hormonal and metabolic pathways.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: D.H., C.M.R., L.J., J.F., and J.G. declare relationships with AstraZeneca (employee/shareholder). The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
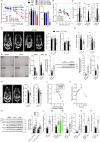
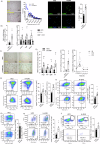
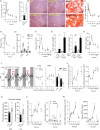
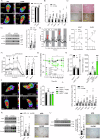
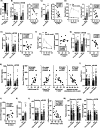
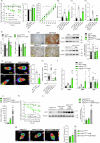

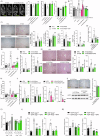
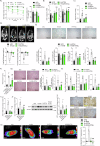
References
-
- Nielsen, M. S. et al. Oxyntomodulin and glicentin may predict the effect of bariatric surgery on food preferences and weight loss. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.105, 1064–1074 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Perakakis, N. et al. Circulating levels of gastrointestinal hormones in response to the most common types of bariatric surgery and predictive value for weight loss over one year: evidence from two independent trials. Metabolism101, 153997 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Baldissera, F. G., Holst, J. J., Knuhtsen, S., Hilsted, L. & Nielsen, O. V. Oxyntomodulin (glicentin-(33-69)): pharmacokinetics, binding to liver cell membranes, effects on isolated perfused pig pancreas, and secretion from isolated perfused lower small intestine of pigs. Regul. Pept.21, 151–166 (1988). - PubMed
-
- Schjoldager, B. T., Baldissera, F. G., Mortensen, P. E., Holst, J. J. & Christiansen, J. Oxyntomodulin: a potential hormone from the distal gut. Pharmacokinetics and effects on gastric acid and insulin secretion in man. Eur. J. Clin. Invest.18, 499–503 (1988). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- PID-2021-122766OB-100/Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness | Agencia Estatal de Investigación (Spanish Agencia Estatal de Investigación)
- RTI2018-094052-B-100/Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness | Agencia Estatal de Investigación (Spanish Agencia Estatal de Investigación)
- PID-2021-122766OB-100/Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness | Agencia Estatal de Investigación (Spanish Agencia Estatal de Investigación)
- P2022/BMD-7227/Comunidad de Madrid
- P2022/BMD-7227/Comunidad de Madrid
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

