Enhanced and sustained biodistribution of HIV-1 neutralizing antibody VRC01LS in human genital and rectal mucosa
- PMID: 39609400
- PMCID: PMC11604655
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-54580-9
Enhanced and sustained biodistribution of HIV-1 neutralizing antibody VRC01LS in human genital and rectal mucosa
Abstract
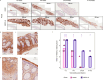
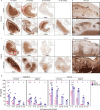
To prevent sexually-acquired HIV-1 infection by immunoprophylaxis, effective concentrations of broadly neutralizing antibodies are likely needed at mucosal sites of exposure. Here, we examine the biodistribution of monoclonal antibody VRC01 and its extended half-life variant, VRC01LS, in colorectal and genitourinary tracts of healthy adults 1-52 weeks after intravenous infusion. At 1-2 weeks, VRC01LS levels are ~3-4 times higher than VRC01 in serum (p = 0.048), rectal (p = 0.067), vaginal (p = 0.003) and cervical tissues (p = 0.003); these differences increase over time. Both antibodies primarily localize within rectal lamina propria and cervicovaginal stroma, with limited and variable epithelial distribution. Although 8-28% of serum mAb levels reach mucosal tissues, <3% are in seminal and rectal secretions. Elimination half-lives in mucosal tissues are 20-28 days for VRC01 and 51-68 days for VRC01LS. Thus, VRC01LS infusion achieves higher, sustained concentrations in human mucosal tissues than VRC01, supporting the future investigation of potent, long-acting LS-modified antibodies to prevent HIV-1.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02797171.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: J.R.M. is listed on patent 9738703 for the VRC01 antibody (patent held by the US National Institutes of Health). M.P., J.H., and S.N. are current employees of the US NIH. All other authors have no competing interests to declare. The study funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

