C/EBPβ-dependent autophagy inhibition hinders NK cell function in cancer
- PMID: 39609420
- PMCID: PMC11604937
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-54355-2
C/EBPβ-dependent autophagy inhibition hinders NK cell function in cancer
Abstract
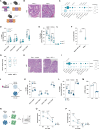
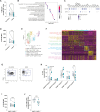
NK cells are endowed with tumor killing ability, nevertheless most cancers impair NK cell functionality, and cell-based therapies have limited efficacy in solid tumors. How cancers render NK cell dysfunctional is unclear, and overcoming resistance is an important immune-therapeutic aim. Here, we identify autophagy as a central regulator of NK cell anti-tumor function. Analysis of differentially expressed genes in tumor-infiltrating versus non-tumor NK cells from our previously published scRNA-seq data of advanced human prostate cancer shows deregulation of the autophagic pathway in tumor-infiltrating NK cells. We confirm this by flow cytometry in patients and in diverse cancer models in mice. We further demonstrate that exposure of NK cells to cancer deregulates the autophagic process, decreases mitochondrial polarization and impairs effector functions. Mechanistically, CCAAT enhancer binding protein beta (C/EBPβ), downstream of CXCL12-CXCR4 interaction, acts as regulator of NK cell metabolism. Accordingly, inhibition of CXCR4 and C/EBPβ restores NK cell fitness. Finally, genetic and pharmacological activation of autophagy improves NK cell effector and cytotoxic functions, which enables tumour control by NK and CAR-NK cells. In conclusion, our study identifies autophagy as an intracellular checkpoint in NK cells and introduces autophagy regulation as an approach to strengthen NK-cell-based immunotherapies.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: T. Tonn is named as an inventor on patents in the field of cancer immunotherapy. The remaining authors declare no competing interests. Ethics statement: This study adheres to the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki and the ethical standards set by our Institution. All human participants provided informed consent, and animal experiments were conducted with approval from the Institutional Animal Care. We promote diversity, equity, and inclusion in research, and we have disclosed any potential conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

