Exploration and practice of potential association prediction between diseases and drugs based on Swanson framework and bioinformatics
- PMID: 39609506
- PMCID: PMC11604654
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-79587-6
Exploration and practice of potential association prediction between diseases and drugs based on Swanson framework and bioinformatics
Abstract
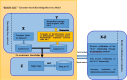
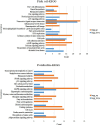
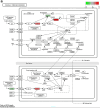
Compared to traditional intermediate concepts, specific bioinformatics entities are more informative and higher directional. This study is based on the BITOLA system and combines bioinformatics methods to determine the intermediate concept which is key to improve efficiency of Literature-based Knowledge Discovery, proposes the concept of "Swanson framework + Bioinformatics", and conducts practice of Literature-based Knowledge Discovery to improve the scientificity and efficiency of research and development. Firstly, detected the disease related genes (i.e. differentially expressed genes) according to the results of gene functional analysis as intermediate concepts to carry out Literature-based Knowledge Discovery. Taking the disease "Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)" as an example, the potential "disease-drug" association was predicted, and the predicted drugs were verified from the perspective of bioinformatics. Two drugs potentially associated with ASD were found: Fish oil and Forskolin, which were closely related to ASD in bioinformatics analysis results and literature verification. The two "disease-drug" association results showed better scientificity. The BIOINF-ABC+ model improves the accuracy of calculations by 76% compared to using the BITOLA system alone. In addition, it also shows high accuracy and credibility in literature verification. The BIOINF-ABC+ model based on the "Swanson framework + Bioinformatics" has good practicality, applicability, and accuracy in conducting "disease-drug" association prediction in the biomedical field, and can be used for mining "disease-drug" relationships.
Keywords: Autism Spectrum disorders; BIOINF-ABC+ model; Differentially expressed genes; Drug Discovery; Literature-based Knowledge Discovery.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Wang, G. H. & Jiang, P. Data mining review. J. Tongji Univ. (Natural Sci. Edition)32, 246–252. 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2004.02.023 (2004). - DOI
-
- Swanson, D. R. & Fish oil, Raynaud’s syndrome, and undiscovered public knowledge. Perspect. Biol. Med.30, 7–18. (1986). 10.1353/pbm.1986.0087 - PubMed
-
- Swanson, D. R. Undiscovered public knowledge. Libr. Q.56, 103–118 (1986). - DOI
-
- Swanson, D. R. Two medical literatures that are logically but not bibliographically connected. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol.38, 228–233 (2010).
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

