Prognostic significance of serum interleukin-6 in severe/critical COVID-19 patients treated with tocilizumab: a detailed observational study analysis
- PMID: 39609511
- PMCID: PMC11605089
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-81028-3
Prognostic significance of serum interleukin-6 in severe/critical COVID-19 patients treated with tocilizumab: a detailed observational study analysis
Abstract
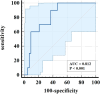
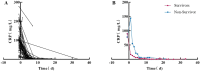
Baseline IL-6 levels have been found to be non-predictive of subsequent outcomes following tocilizumab treatment, highlighting the need for more reliable predictive markers. To address this, a retrospective analysis was conducted on the clinical profiles, diagnostic tests, and follow-up prognoses of 60 patients with severe or critical COVID-19, all of whom were identified as experiencing a cytokine storm and subsequently received tocilizumab treatment. Among the patients, the overall survival rate during follow-up was 80%, with further analysis revealing that advanced age was an independent risk factor for adverse outcomes. Following tocilizumab administration, a statistically significant increase in IL-6 and D-dimer levels was observed, while markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP), procalcitonin (PCT), and fibrinogen demonstrated reductions compared to pre-treatment values. Specifically, IL-6 levels initially surged briefly after tocilizumab intervention before gradually diminishing. To assess the prognostic utility of IL-6, the Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve was employed, which yielded an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.812, indicating strong predictive capability, with a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 53.49%. The optimal cut-off value for IL-6 was identified at 147.79 pg/mL. In conclusion, IL-6 levels tend to rise transiently following tocilizumab therapy, before gradually declining. These post-treatment IL-6 measurements may serve as a valuable biomarker for assessing prognosis in patients undergoing this treatment.
Keywords: COVID-19; IL6; Prognosis; Tocilizumab.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Trajectories and predictive significance of inflammatory parameters for clinical outcome in COVID-19 patients treated with tocilizumab.Infection. 2025 Feb;53(1):339-348. doi: 10.1007/s15010-024-02375-x. Epub 2024 Aug 29. Infection. 2025. PMID: 39210228 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of inflammatory biomarkers in patients with COVID-19 infections: Bahrain experience.Biomark Med. 2021 Jun;15(8):541-549. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2020-0422. Epub 2021 May 14. Biomark Med. 2021. PMID: 33988463 Free PMC article.
-
Differences of inflammatory and non-inflammatory indicators in Coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) with different severity.Infect Genet Evol. 2020 Nov;85:104511. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104511. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Infect Genet Evol. 2020. PMID: 32858231 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical outcomes in COVID-19 patients treated with tocilizumab: An individual patient data systematic review.J Med Virol. 2020 Nov;92(11):2516-2522. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26038. Epub 2020 Jun 9. J Med Virol. 2020. PMID: 32436994 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and prognostic value of hematological and immunological markers in COVID-19 infection: A meta-analysis of 6320 patients.PLoS One. 2020 Aug 21;15(8):e0238160. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238160. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32822430 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Evaluating the efficacy of different doses of tocilizumab in treating critically ill COVID-19 patients: a single-center retrospective cohort study.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 24;16:1571372. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1571372. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40777985 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

