The expression profile analysis and functional prediction of lncRNAs in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in maintenance hemodialysis patients developing heart failure
- PMID: 39609580
- PMCID: PMC11604924
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-81080-z
The expression profile analysis and functional prediction of lncRNAs in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in maintenance hemodialysis patients developing heart failure
Abstract
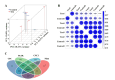
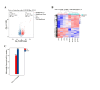
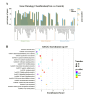
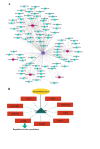
Heart failure (HF) is the leading cause of death in patients with maintenance hemodialysis (MHD). Biomarkers has an important guiding role in the early diagnosis, risk stratification, and prognostic assessment of HF. Increasing studies have indicated that long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have played an indispensable role in the regulatory network of HF. This study was aiming to explore the expression profiles of lncRNAs in patients treated with MHD developing heart failure. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated from 4 hemodialysis patients with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and 4 hemodialysis patients with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), respectively. The expression profile analysis of lncRNAs was performed by using Illumina Novaseq 6000 sequencer. Quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was used to verify the expression of representative differentially expressed lncRNAs. Based on lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA-KEGG network analysis, the potential role of candidate lncRNAs and their association with the severity of HF were further evaluated. In total, 1,429 differentially expressed lncRNAs were found between patients with HFrEF and patients with HFpEF, of which 613 were up-regulated and 816 were down-regulated (P < 0.05). Five candidate lncRNAs were screened out by a series of bioinformatic analyses. After being compared with miRBase, ENST00000561762, one of the 5 candidates, was considered the most likely lncRNA to be serving as a precursor for miRNA. Nine predicted target genes were found by further lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA-KEGG network analysis, and among which ITGB5 was enriched in the actin dynamics signaling pathway. In another cohort of hemodialysis patients, the expression of lncRNA ENST00000561762 was verified by qRT-PCR. Further analysis revealed that there was a strong correlation between left ventricular ejection fraction and ENST00000561762, proBNP, and 6-minute walk distance, respectively. LncRNAs expression profile was remarkably different in hemodialysis patients with HFrEF compared to those with HFpEF. Among which, lncRNA ENST00000561762 was considered as a promising biomarker for patients with HFrEF as it was predicted to be a miRNA precursor to regulate the actin dynamics signaling pathway.
Keywords: HF; MHD; PBMC; lncRNAs.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Statement of ethics: This study adhered to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki and Malaysian Guidelines for Good Clinical Practice (GCP).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exosomal lncRNA profiles in patients with HFrEF: Evidence for KLF3-AS1 as a novel diagnostic biomarker.Mol Cell Probes. 2025 Aug;82:102032. doi: 10.1016/j.mcp.2025.102032. Epub 2025 May 20. Mol Cell Probes. 2025. PMID: 40404068
-
Comprehensive analysis of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA networks during osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.BMC Genomics. 2022 Jun 7;23(1):425. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08646-x. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35672672 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of molecular signatures in epicardial adipose tissue in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.ESC Heart Fail. 2024 Oct;11(5):2510-2520. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14748. Epub 2024 Mar 8. ESC Heart Fail. 2024. PMID: 38454838 Free PMC article.
-
Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction (HFrEF) and Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF): The Diagnostic Value of Circulating MicroRNAs.Cells. 2019 Dec 16;8(12):1651. doi: 10.3390/cells8121651. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31888288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating Non-Coding RNAs as Indicators of Fibrosis and Heart Failure Severity.Cells. 2025 Apr 7;14(7):553. doi: 10.3390/cells14070553. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40214506 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Associations of circulating omentin-1 levels and long noncoding RNA MALAT1 expression with coronary heart disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Sci Rep. 2025 May 11;15(1):16376. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-01153-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40350526 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

