Cerebral magnetic resonance spectroscopy - insights into preterm brain injury
- PMID: 39609610
- PMCID: PMC11825355
- DOI: 10.1038/s41372-024-02172-2
Cerebral magnetic resonance spectroscopy - insights into preterm brain injury
Abstract
Objective: Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) may provide clinically relevant data regarding metabolic processes that govern the course of preterm brain injury.
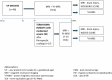
Study design: 46 very preterm infants (VP) were evaluated by magnetic resonance imaging and 1H-MRS at term-equivalent age. Brain injury was assessed according to the Kidokoro scale. Moreover, 17 term-born infants with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) were scanned. The metabolic profile of the central nervous system was obtained from the bilateral thalamus.
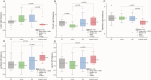
Result: The Lipids/Creatine, Choline/Creatine, N-acetyl aspartate/Choline, Lactate/N-acetyl aspartate, and Lactate/Creatine ratios differed between VP infants with moderate+severe brain damage and those without brain injury. Moreover, VP infants with moderate+severe brain damage had higher Lactate/ N-acetyl aspartate and Lactate/Creatine ratios than HIE group.
Conclusion: There were significant differences in the cerebral metabolite profile at TEA between VP infants with and without brain injury. The 1H-MRS profile of VP infants with moderate+severe brain damage may reflect profound chronic metabolic alterations.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Statement of ethics: This study protocol was reviewed and approved by the Jagiellonian University Bioethical Committee, Krakow, Poland (approval number 1072.6120.336.2020). Written informed consent was obtained from the participants’ parents for participation in the study. All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Lally PJ, Montaldo P, Oliveira V, Soe A, Swamy R, Bassett P, et al. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy assessment of brain injury after moderate hypothermia in neonatal encephalopathy: a prospective multicentre cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18:35–45. 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30325-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources