Epigenetic regulation of organ-specific functions in Mikania micrantha and Mikania cordata: insights from DNA methylation and siRNA integration
- PMID: 39609688
- PMCID: PMC11605950
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-024-05858-z
Epigenetic regulation of organ-specific functions in Mikania micrantha and Mikania cordata: insights from DNA methylation and siRNA integration
Abstract
Background: DNA methylation is a crucial epigenetic mechanism that regulates gene expression during plant growth and development. However, the role of DNA methylation in regulating the organ-specific functions of the invasive weed Mikania micrantha remains unknown.
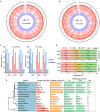
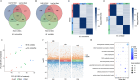
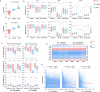
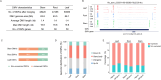
Results: Here, we generated DNA methylation profiles for M. micrantha and a local congeneric species, Mikania cordata, in three vegetative organs (root, stem, and leaf) using whole-genome bisulfite sequencing. The results showed both differences and conservation in methylation levels and patterns between the two species. Combined with transcriptome data, we found that DNA methylation generally inhibited gene expression, with varying effects depending on the genomic region and sequence context (CG, CHG, and CHH). Genes overlapping with differentially methylated regions (DMRs) were more likely to be differentially expressed between organs, and DMR-associated upregulated differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were enriched in organ-specific pathways. A comparison between photosynthetic (leaf) and non-photosynthetic (root) organs of M. micrantha further confirmed the regulatory role of DNA methylation in leaf-specific photosynthesis. Integrating small RNA-Seq data revealed that 24-nt small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) were associated with CHH methylation in gene-rich regions and regulated CHH methylation in the flanking regions of photosynthesis-related genes.
Conclusion: This study provides insights into the complex regulatory role of DNA methylation and siRNAs in organ-specific functions and offers valuable information for exploring the invasive characteristics of M. micrantha from an epigenetic perspective.
Keywords: Mikania cordata; Mikania micrantha; DNA methylation; siRNA.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Slotkin RK, Martienssen R. Transposable elements and the epigenetic regulation of the genome. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8(4):272–85. - PubMed
-
- Robertson KD. DNA methylation and human disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2005;6(8):597–610. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X, Yazaki J, Sundaresan A, Cokus S, Chan SW, Chen H, Henderson IR, Shinn P, Pellegrini M, Jacobsen SE, et al. Genome-wide high-resolution mapping and functional analysis of DNA methylation in arabidopsis. Cell. 2006;126(6):1189–201. - PubMed
-
- Zhang H, Lang Z, Zhu JK. Dynamics and function of DNA methylation in plants. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(8):489–506. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 31872670/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2021A1515010911/Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 202206010107/Science and Technology Projects in Guangzhou
- JCYJ20210324141000001/Project of Department of Science and Technology of Shenzhen City, Guangdong
- JCYJ20230807110359040/Project of Department of Science and Technology of Shenzhen City
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

