Serum proteome profiling reveals HGFA as a candidate biomarker for pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 39609799
- PMCID: PMC11603967
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-024-03036-1
Serum proteome profiling reveals HGFA as a candidate biomarker for pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
Background: Identification and validation of potential biomarkers could facilitate the identification of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) and thus aid to study their roles in the disease process.
Methods: We used the isobaric tag for relative and absolute quantitation approaches to compare the protein profiles between the serum of PAH patients and the controls. Bioinformatics analyses and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) identification of PAH patients and the controls were performed to identify the potential biomarkers. The receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) analysis was used to evaluate the diagnostic performance of these potential biomarkers. Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis further clarified the relationship between the potential biomarkers and PAH. Additionally, the expression levels of the potential biomarkers were further validated in two PAH animal models (monocrotaline-PH and Sugen5416 plus hypoxia-PH) using ELISA and reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR).
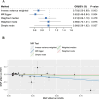
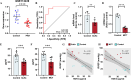
Results: We identified significant changes in three proteins including heparanase (HPSE), gelsolin (GSN), and hepatocyte growth factor activator (HGFA) in PAH patients. The ROC analysis showed that the areas under the curve of HPSE, GSN, and HGFA in differentiating PAH patients from controls were 0.769, 0.777, and 0.964, respectively. HGFA was correlated with multiple parameters of right ventricular functions in PAH patients. Besides proteomic analysis, we also used MR method to demonstrate the causal link between genetically reduced HGFA levels and an increased risk of PAH. In subsequent validation study in PAH animal models, the mRNA expression levels of HGFA in the lung tissues were significantly lower in PAH rat models than in controls. In the rat models, serum levels of HGFA were lower compared to the control group and showed a negative correlation with right ventricular systolic pressure.
Conclusion: The study demonstrated that HGFA might be a promising biomarker for noninvasive detection of PAH.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Isobaric tag for relative and absolute quantitation; Proteomics; Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study's ethical approval (patients and animals) was obtained from the Ethics Committee in China-Japan Friendship Hospital. All the participants provided informed consent and agreed to participate in this research. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ruopp NF, Cockrill BA. Diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension: a review. JAMA. 2022;327(14):1379–91. - PubMed
-
- Hassoun PM. Pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(25):2361–76. - PubMed
-
- Boucly A, Weatherald J, Savale L, Jaïs X, Cottin V, Prevot G, et al. Risk assessment, prognosis and guideline implementation in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Respir J. 2017;50(2):1700889. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2021-I2M-1-049/Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences
- 2021-I2M-1-061/Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences
- 2022-NHLHCRF-LX-01-0203/National High Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding
- ZRJY2023-QM31/Elite Medical Professionals project of China-Japan Friendship Hospital
- 2023-ZF-22/Institute of Respiratory Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Foundation for Young Scholars
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

