Knockdown of RUVBL2 improves hnRNPA2/B1-stress granules dynamics to inhibit perioperative neurocognitive disorders in aged mild cognitive impairment rats
- PMID: 39610020
- PMCID: PMC11896576
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.14418
Knockdown of RUVBL2 improves hnRNPA2/B1-stress granules dynamics to inhibit perioperative neurocognitive disorders in aged mild cognitive impairment rats
Abstract
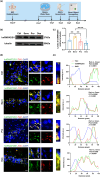
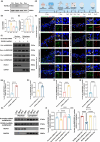
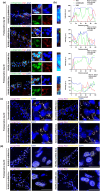
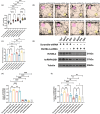
Perioperative neurocognitive disorders (PND) is common in aged mild cognitive impairment (MCI) patients and can accelerate the progression to dementia. This process involves heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1 (hnRNPA2/B1)-mediated aggregates of stress granules (SGs), while RUVBL2 influences the dynamics of these SGs. Our research explored a new target for modulating hnRNAPA2/B1-SGs dynamics to accelerate their disassembly and potentially delay MCI progression due to PND. We assessed the effect of hippocampal RUVBL2 knockdown on hnRNPA2/B1-SGs in aged MCI rats through behavioral studies, biochemical experiments and MRI. We also examined hnRNPA2/B1-SGs dynamics using immunofluorescence staining and fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) in rat primary hippocampal neurons. Our results revealed that hnRNPA2/B1 in the hippocampus of aged MCI rats translocates to the cytoplasm to form SGs following anesthesia. RUVBL2 knockdown promotes the disappearance of hnRNPA2/B1-SGs, allowing hnRNPA2/B1 to return to the nucleus and enhancing functional activity in the brain regions of aged MCI rats. In primary hippocampal neurons, RUVBL2 deletion facilitated hnRNPA2/B1-SGs transition from hydrogel to liquid, promoting disassembly. We compared three commonly used general anesthetics-3% sevoflurane, 40 mg·kg-1·h-1 propofol, and 9% desflurane. Sevoflurane upregulated RUVBL2, which decreased the intraneuronal pH and disrupted energy metabolism. These changes resulted in greater stabilization of hnRNPA2/B1- SGs. In conclusion, our findings indicated that the knockdown of RUVBL2 expression contributes to the transition of hnRNPA2/B1-SGs from the hydrogel phase to the liquid phase. Targeted interference with RUVBL2 may represent a novel approach to delay the progression to dementia due to PND in aged MCI patients.
Keywords: RUVBL2; aged mild cognitive impairment; dynamics; hnRNPA2/B1; perioperative neurocognitive disorders; stress granules.
© 2024 The Author(s). Aging Cell published by the Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Kapβ2 Reverses Sevoflurane-Induced Hydrogel Phase Transition of hnRNPA2/B1-SG in Hypoxic Primary Rat Hippocampal Neurons.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Aug;31(8):e70532. doi: 10.1111/cns.70532. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 40776395 Free PMC article.
-
Kapβ2 Inhibits Perioperative Neurocognitive Disorders in Rats with Mild Cognitive Impairment by Reversing the Nuclear-Cytoplasmic Mislocalization of hnRNPA2/B1.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Jul;61(7):4488-4507. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03789-8. Epub 2023 Dec 16. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38102516
-
Kapβ2 attenuates post-anesthetic neurocognitive dysfunction by resolving HnRNPA2/B1 fibrillary tangles in a rat model of mild cognitive impairment.Exp Neurol. 2025 Aug 12:115426. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2025.115426. Online ahead of print. Exp Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40812499
-
Decoding stress granules dynamics: Implications for neurodegenerative disease.Prog Neurobiol. 2025 May;248:102758. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2025.102758. Epub 2025 Mar 23. Prog Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40132681 Review.
-
Biogenesis of stress granules and their role in the regulation of stress-induced male reproduction disorders.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Feb 13;23(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02054-w. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 39948590 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cao, S. J. , Zhang, Y. , Zhang, Y. X. , Zhao, W. , Pan, L. H. , Sun, X. D. , Jia, Z. , Ouyang, W. , Ye, Q. S. , Zhang, F. X. , Guo, Y. Q. , Ai, Y. Q. , Zhao, B. J. , Yu, J. B. , Liu, Z. H. , Yin, N. , Li, X. Y. , Ma, J. H. , Li, H. J. , … Wang, D. X. (2023). Delirium in older patients given propofol or sevoflurane anaesthesia for major cancer surgery: A multicentre randomised trial. British Journal of Anaesthesia, 131(2), 253–265. 10.1016/j.bja.2023.04.024 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen, B. , Qin, G. , Xiao, J. , Deng, X. , Lin, A. , & Liu, H. (2022). Transient neuroinflammation following surgery contributes to long‐lasting cognitive decline in elderly rats via dysfunction of synaptic NMDA receptor. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 19(1), 181. 10.1186/s12974-022-02528-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

