Diabetic neuropathy: understanding the nexus of diabetic neuropathy, gut dysbiosis and cognitive impairment
- PMID: 39610501
- PMCID: PMC11599548
- DOI: 10.1007/s40200-024-01447-x
Diabetic neuropathy: understanding the nexus of diabetic neuropathy, gut dysbiosis and cognitive impairment
Abstract
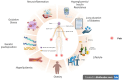
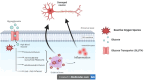
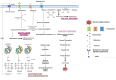
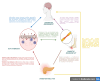
Objectives: Diabetic neuropathy is a traditional and one of the most prevalent complications of diabetes mellitus. The exact pathophysiology of diabetic neuropathy is not fully understood. However, oxidative stress and inflammation are proven to be one of the major underlying mechanisms of neuropathy which is described in detail. Gut dysbiosis is being studied for various neurological disorders and its impact on diabetic neuropathy is also explained. Diabetic neuropathy also causes loss in an individual's quality of life and one such adverse event is cognitive dysfunction. The interrelation between the neuropathy, cognitive dysfunction and gut is reviewed.
Methods: The exact mechanism is not understood but several hypotheses, cross-sectional studies and systematic reviews suggest a relationship between cognition and neuropathy. The review has collected data from various review and research publications that justifies this inter-relationship.
Results: The multifactorial etiology and pathophysiology of diabetic neuropathy is described with special emphasis on the role of gut dysbiosis. There might exist a correlation between the neuropathy and cognitive impairment caused simultaneously in diabetic patients.
Conclusions: This review summarizes the relationship that might exist between diabetic neuropathy, cognitive dysfunction and the impact of disturbed gut microbiome on its development and progression.
Keywords: Cognitive impairment; Diabetic neuropathy; Gut dysbiosis; Gut microbiome; Inflammation; Oxidative stress.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Tehran University of Medical Sciences 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures

References
-
- IDF DIABETES, ATLAS. 2021.
-
- Grover M, Makkar R, Sehgal A, Seth SK, Gupta J, Behl T. Etiological aspects for the occurrence of Diabetic Neuropathy and the suggested measures. Neurophysiology. 2020;52:159–68.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

