Crosstalk of pyroptosis and cytokine in the tumor microenvironment: from mechanisms to clinical implication
- PMID: 39614288
- PMCID: PMC11607834
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-024-02183-9
Crosstalk of pyroptosis and cytokine in the tumor microenvironment: from mechanisms to clinical implication
Abstract
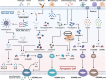
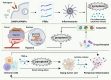
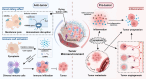
In the realm of cancer research, the tumor microenvironment (TME) plays a crucial role in tumor initiation and progression, shaped by complex interactions between cancer cells and surrounding non-cancerous cells. Cytokines, as essential immunomodulatory agents, are secreted by various cellular constituents within the TME, including immune cells, cancer-associated fibroblasts, and cancer cells themselves. These cytokines facilitate intricate communication networks that significantly influence tumor initiation, progression, metastasis, and immune suppression. Pyroptosis contributes to TME remodeling by promoting the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and sustaining chronic inflammation, impacting processes such as immune escape and angiogenesis. However, challenges remain due to the complex interplay among cytokines, pyroptosis, and the TME, along with the dual effects of pyroptosis on cancer progression and therapy-related complications like cytokine release syndrome. Unraveling these complexities could facilitate strategies that balance inflammatory responses while minimizing tissue damage during therapy. This review delves into the complex crosstalk between cytokines, pyroptosis, and the TME, elucidating their contribution to tumor progression and metastasis. By synthesizing emerging therapeutic targets and innovative technologies concerning TME, this review aims to provide novel insights that could enhance treatment outcomes for cancer patients.
Keywords: Clinical implication; Cytokine; Mechanism; Pyroptosis; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2024ZZTS0961/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Central South University
- 82272664, 82172500, 32300528/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82272664, 82172500, 32300528/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2023RC3085, 2023RC3080/Science and Technology Innovation Program of Hunan Province
- 2023RC3085, 2023RC3080/Science and Technology Innovation Program of Hunan Province
- 23B0023/the Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department
- 2024JJ2084/Excellent Youth Foundation of Hunan Scientific Committee
- R2023054/Hunan Provincial Health High-Level Talent Scientific Research Project
- 2022JJ30843/Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2021Szvup169/Science and Technology Development Fund Guided by Central Government
- D2022117/Hunan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Project
- B202304077077/Scientific Research Program of Hunan Provincial Health Commission
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

