Targeting PRMT5 through PROTAC for the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer
- PMID: 39614393
- PMCID: PMC11607928
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-024-03237-y
Targeting PRMT5 through PROTAC for the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is currently the most aggressive subtype of breast cancer, characterized by high heterogeneity and strong invasiveness, and currently lacks effective therapies. PRMT5, a type II protein arginine methyltransferase, is upregulated in numerous cancers, including TNBC, and plays a critical role, marked it as an attractive therapeutic target. PROTAC (Proteolysis Targeting Chimeras) is an innovative drug development technology that utilizes the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) to degrade target proteins, which is characterized by higher activity, enhanced safety, lower resistance, and reduced toxicity, offering significant value for clinical translation.
Methods: This study utilizes the PROTAC technology to develop potential degraders targeting PRMT5 in vitro and in vivo.
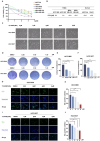
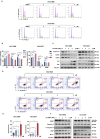
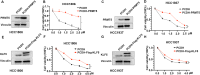
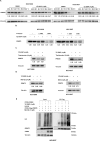
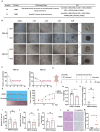
Results: Through the design, synthesis and screening of a series of targeted compounds, we identified YZ-836P as an effective compound that exerted cytotoxic effects and reduced the protein levels of PRMT5 and its key downstream target protein KLF5 in TNBC after 48 h. Its efficacy was significantly superior to the PRMT5 PROTAC degraders that had been reported. YZ-836P induced G1 phase cell cycle arrest and significantly induced apoptosis in TNBC cells. Additionally, we demonstrated that YZ-836P promoted the ubiquitination and degradation of PRMT5 in a cereblon (CRBN)-dependent manner. Notably, YZ-836P exhibited pronounced efficacy in inhibiting the growth of TNBC patient-derived organoids and xenografts in nude mice.
Conclusions: These findings position YZ-836P as a promising candidate for advancing treatment modalities for TNBC.
Trial registration: Ethics Committee of Yunnan Cancer Hospital, KYCS2023-078. Registered 7 June 2023.
Keywords: KLF5; PRMT5; PROTAC; TNBC.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The animal experiment followed the ARRIVE guidelines and had been approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the Kunming Medical University (kmmu20240729). Additionally, the patient-derived organoids assays conformed the Declaration of Helsinki and had been approved by the Ethics Committee of Yunnan Cancer Hospital (KYCS2023-078). Consent for publication: All the authors consent for publication. Competing interests: The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Lin NU, Vanderplas A, Hughes ME, Theriault RL, Edge SB, Wong YN, Blayney DW, Niland JC, Winer EP, Weeks JC. Clinicopathologic features, patterns of recurrence, and survival among women with triple-negative breast cancer in the National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Cancer. 2012;118(22):5463–72. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cortes J, Rugo HS, Cescon DW, Im SA, Yusof MM, Gallardo C, Lipatov O, Barrios CH, Perez-Garcia J, Iwata H, et al. Pembrolizumab plus Chemotherapy in Advanced Triple-negative breast Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(3):217–26. - PubMed
-
- Bardia A, Hurvitz SA, Tolaney SM, Loirat D, Punie K, Oliveira M, Brufsky A, Sardesai SD, Kalinsky K, Zelnak AB, et al. Sacituzumab Govitecan in Metastatic Triple-negative breast Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(16):1529–41. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2020YFA0112300/National Key R&D Program of China
- 2023ZD0502200/National Key R&D Program of China
- 2023YFA1800403/National Key R&D Program of China
- 82060548/National Science Foundation of China
- 82203878/National Science Foundation of China
- 82302957/National Science Foundation of China
- U2102203/National Science Foundation of China
- 82430084/National Science Foundation of China
- 82072914/National Science Foundation of China
- 82473762/National Science Foundation of China
- 2023M731011/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- 2023M731448/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- GZC20240483/Postdoctoral Fellowship Program of CPSF
- 202302AA310046/Biomedical Projects of Yunnan Key Science and Technology Program
- 202502AA310002/Biomedical Projects of Yunnan Key Science and Technology Program
- 202101AY070001-083/Yunnan Provincial Department of Science and Technology
- 202401AY070001-026/Joint Special Funds for the Department of Science and Technology of Yunnan Province-Kunming Medical University
- 202401CF070054/Yunnan Fundamental Research Projects
- 202201BC070002/Yunnan Fundamental Research Projects
- Yunnan Revitalization Talent Support Program/Yunnan Revitalization Talent Support Program
- Q7YSZJGZZ-2020025/Yunnan (Kunming) Academician Expert Workstation
- 202405AS350016/the Innovative Research Team of Yunnan Province
- 2023BEG02010/Regional Key R&D Program of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

