Real-Life Functioning in 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome in Relation to Neurocognitive Abilities and Psychotic Symptoms: A Comparison With Idiopathic Schizophrenia
- PMID: 39614621
- PMCID: PMC11791388
- DOI: 10.1111/jir.13200
Real-Life Functioning in 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome in Relation to Neurocognitive Abilities and Psychotic Symptoms: A Comparison With Idiopathic Schizophrenia
Abstract
Background: The 22q11.2 deletion syndrome (22q11.2DS) entails intellectual disabilities and higher risk of psychotic disorders. Neurocognitive deficits predict real-life functioning of schizophrenic patients. We investigated real-life functioning in 22q11.2DS, aiming at defining how neurocognitive profile and psychopathological variables impact on psychotic patients' social functioning.
Methods: We recruited 63 patients with schizophrenia (SCZ, N = 63), 44 with 22q11.2DS (DEL, N = 44) and 19 with 22q11.2DS and psychosis (DEL-SCZ, N = 19), all matched for age, sex and neurocognitive profile; we administered the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS), the Brief Negative Symptom Scale (BNSS), the Specific Levels of Functioning (SLoF) scale and the Measurement and Treatment Research to Improve Cognition in Schizophrenia Consensus Cognitive Battery (MCCB). We implemented descriptive analyses, MANCOVA and linear regression statistics.
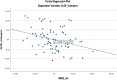
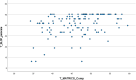
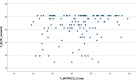
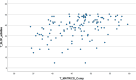
Results: The DEL-SCZ and the SCZ groups showed similar levels in Interpersonal Relationships (p = 0.093) and Social Acceptability subscales (p = 0.283). The DEL group scored higher on the Interpersonal Relationships subscale compared with the SCZ group (p = 0.001). The groups scored similarly on the other SLoF subscales. Both BNSS total score (beta = -0.343; p = 0.004) and BNSS asociality (beta = -0.487; p = 0.038) significantly predicted the Interpersonal Relationships variable in the groups with psychosis (SCZ and DEL-SCZ).
Discussion and conclusions: Individuals with 22q11.2DS display a similar real-life functioning to patients with chronic schizophrenia. Social functioning impairments are typical of psychosis regardless of the genetic condition and highly predicted by negative symptoms like asociality. The 22q11.2DS represents a reliable biological model to study vulnerability to psychosis and its consequences on patients' real-life and social functioning.
Keywords: 22q11.2 deletion syndrome; neurocognition; psychosis; real‐life functioning; schizophrenia; social functioning.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Intellectual Disability Research published by John Wiley & Sons and MENCAP.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Accinni, T. , Buzzanca A., Frascarelli M., et al. 2022. “Social Cognition Impairments in 22q11.2DS Individuals With and Without Psychosis: A Comparison Study With a Large Population of Patients With Schizophrenia.” Schizophrenia Bulletin Open 3: sgab049. 10.1093/schizbullopen/sgab049. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ardinger, H. H. , and Ardinger R. H.. 2002. “Clinical Presentation of Velo‐Cardio‐Facial Syndrome.” Progress in Pediatric Cardiology 15: 93–97. 10.1016/S1058-9813(02)00032-2. - DOI
-
- Bamforth, S. D. , and Burn J.. 2013. “DiGeorge Syndrome.” In Brenner's Encyclopedia of Genetics, vol. 319–321, Second ed. New York, San Diego: Academic Press. 10.1016/B978-0-12-374984-0.00402-2. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

