Modulating the tumor microenvironment in a mouse model of colon cancer using a combination of HIF-1α inhibitors and Toll-Like Receptor 7 agonists
- PMID: 39614894
- PMCID: PMC11985627
- DOI: 10.1007/s00210-024-03658-8
Modulating the tumor microenvironment in a mouse model of colon cancer using a combination of HIF-1α inhibitors and Toll-Like Receptor 7 agonists
Abstract
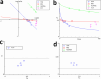
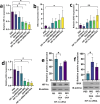
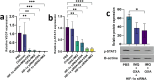
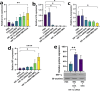
The immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) plays a pivotal role in the response to various anticancer therapies, such as immune and chemotherapeutic agents. In this study, the synergistic effects of gene-targeting HIF-1α siRNA combined with Toll-Like Receptor 7 agonist on TME remodeling were investigated in a mouse model of colorectal cancer (CRC). A HIF-1α-specific siRNA duplex was formulated based on the ionic gelation of tripolyphosphate (TPP) with cationic chitosan (CH) as a nanoplex and evaluated in terms of size, charge, polydispersity index and gel retardation assay. MTT assay was conducted to assess the cytotoxicity of the specific siRNA duplex against CT26 cells. Hypoxic condition was generated to evaluate the gene and protein expression levels of HIF-1α, respectively. CT26 mouse model was established to assess the synergistic effect of silencing HIF-1α combined with oxaliplatin (OXA) and imiquimod (IMQ) on tumor growth. The mean diameter of the CH/siRNA nanoparticles was 243 ± 6 nm, as confirmed with Micrograph scanning electron microscope. There were no significant differences observed between the CT26 cells treated with nanoparticles alone and the untreated cells, indicating that these nanoparticles are safe and physiologically biocompatible (p ≥ 0.05). Triple combination therapy involving HIF-1α siRNA, OXA, and IMQ significantly retarded tumor growth and led to elevated levels of cytokines linked to cellular immunity (INF-γ and IL-12) compared with those in the other groups (P < 0.05). The positive correlation coefficient (r = 0.68) between tumor size and HIF-1α expression levels was statistically significant (P = 0.003). Compared with those in the control group, the expression levels of the anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10 and IL-4 significantly decreased (P < 0.05). In conclusion, our findings suggest that inhibiting HIF-1α could serve as a rational strategy to enhance the antitumor response in the TME.
Keywords: Chemotherapy; Colorectal cancer; Combination therapy; Gene therapy; HIF-1α; Immunotherapy; TLR; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics statement: Institutional Review Board Statement: All animal procedures were conducted in accordance with the ethical guidelines set forth by the National Institutes of Health guidelines, as approved by the Tabriz University of Medical Sciences (IR.TBZMED.VCR.REC.1399.056). Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Targeting hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha augments synergistic effects of chemo/immunotherapy via modulating tumor microenvironment in a breast cancer mouse model.Bioimpacts. 2024 Sep 10;15:30424. doi: 10.34172/bi.30424. eCollection 2025. Bioimpacts. 2024. PMID: 40256236 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous blockade of TIGIT and HIF-1α induces synergistic anti-tumor effect and decreases the growth and development of cancer cells.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Dec;101(Pt A):108288. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108288. Epub 2021 Oct 29. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34710844
-
Targeting aerobic glycolysis and HIF-1alpha expression enhance imiquimod-induced apoptosis in cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2014 Mar 15;5(5):1363-81. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1734. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 24658058 Free PMC article.
-
Codelivery of HIF-1α siRNA and Dinaciclib by Carboxylated Graphene Oxide-Trimethyl Chitosan-Hyaluronate Nanoparticles Significantly Suppresses Cancer Cell Progression.Pharm Res. 2020 Sep 17;37(10):196. doi: 10.1007/s11095-020-02892-y. Pharm Res. 2020. Retraction in: Pharm Res. 2022 Dec;39(12):3383-3384. doi: 10.1007/s11095-022-03432-6. PMID: 32944844 Retracted.
-
Blockade of HIF-1α and STAT3 by hyaluronate-conjugated TAT-chitosan-SPION nanoparticles loaded with siRNA molecules prevents tumor growth.Nanomedicine. 2021 Jun;34:102373. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2021.102373. Epub 2021 Mar 3. Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33667724
References
-
- Ahmadian S et al (2021) Sensitization of A-549 lung cancer cells to Cisplatin by Quinacrine-loaded lipidic nanoparticles via suppressing Nrf2 mediated defense mechanism. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 394:1521–1528 - PubMed
-
- Alhazami AJZ, Pouresmaeil V, Homayouni Tabrizi M (2024) The Methylurolithin A-loaded PLGA-Folate-Chitosan Nanoparticles (Mu-PFCNPs), as the novel safe selective anti-colon cancer drug delivery system. J Clust Sci 35:1719–1730
-
- Aznar MA et al (2017) Intratumoral delivery of immunotherapy—act locally, think globally. J Immunol 198(1):31–39 - PubMed

