Salivary Gland Oncocytomas. A Systematic Review
- PMID: 39614964
- PMCID: PMC11608208
- DOI: 10.1007/s12105-024-01730-6
Salivary Gland Oncocytomas. A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: Oncocytoma is a primary benign epithelial neoplasm comprising less than 2% of salivary tumors with a low recurrence rate.
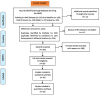
Methods: A systematic review of documented case reports and case series of oncocytomas is presented. Searches from different databases were performed to identify articles from 1956 to 2024. The variables included were gender, age, symptoms, duration time before diagnosis, type of gland, histological features, special or immunohistochemical evaluation, treatment, follow-up, recurrence, and relation with a medical condition or syndrome.
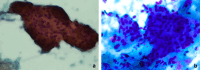
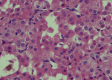
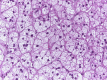
Results: Of the 147 cases reported, 53.1% affected females, and 46.9% were in males. The average age was 58.7 years, and the mean size was 2.3 cm. The most common clinical presentation was swelling (92.6%) and 66.7% were asymptomatic. The parotid was the most commonly affected gland with 66% of cases, the submandibular gland with 23.3%, and the minor salivary glands with Phosphotungstic acid-hematoxylin (PTAH) was the most common special stain used in 36.7%, followed by a combination with Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) with and without diastase in 26.6%. Excisional biopsy was the most common treatment in 38.1% followed by superficial parotidectomy in 32.7%. Follow-up was 34.7 months on average. Bilateral oncocytomas were found in 4.8% with a 6 to 1 female-male proportion. Recurrence was found in 2.7% and association with Birt-Hogg-Dube (BHD) syndrome was 8.2%.
Conclusion: Salivary oncocytoma is a rare epithelial neoplasm with nonspecific clinical presentations. Diagnosis can be suspected on cytology and confirmed by histologic examination. The lesion has an indolent clinical course and most of the reported cases did not recur. There seems to be an association between bilateral oncocytomas and females and a low but interesting association with BHD. Overall, this review serves to better highlight the features of this rare benign neoplasm.
Keywords: Oncocytoma; Oxyphilic adenoma; Parotid gland; Salivary gland; Salivary tumors; Submandibular gland.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Gasparre G, Romeo G, Rugolo M, Porcelli AM (2011) Learning from oncocytic tumors: why choose inefficient mitochondria? Biochem Biophys Acta 1807:633–642 - PubMed
-
- Beal KP, Singh B, Kraus D, Yahalom J, Portlock C, Wolden SL (2003) Radiation-induced salivary gland tumors: a report of 18 cases and a review of the literature. Cancer J 9(6):467–471. 10.1097/00130404-200311000-00006 - PubMed
-
- Capone RB, Ha PK, Westra WH, Pilkington TM, Sciubba JJ, Koch WM (2002) Oncocytic neoplasms of the parotid gland: a 16-year institutional review. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 126(6):657–662 - PubMed
-
- Kontaxis A, Zanarotti U, Kainz J, Beham A (2004) Diffuse hyperplastic oncocytosis of the parotid gland. Laryngorhinootologie 83:185–188 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

