Rare case of postpartum septic arthritis of the shoulder caused by multi-drug resistant Kingella kingae: A case report
- PMID: 39615251
- PMCID: PMC11648235
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2024.110649
Rare case of postpartum septic arthritis of the shoulder caused by multi-drug resistant Kingella kingae: A case report
Abstract
Introduction: Septic arthritis is a severe joint infection that can cause permanent damage if not promptly treated. Although the shoulder is an uncommon site for this condition, Kingella kingae, typically associated with pediatric infections, can occasionally be a causative agent. Postpartum septic arthritis is rare, making this case particularly unique.
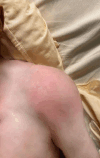
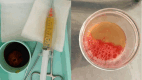
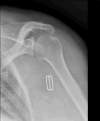
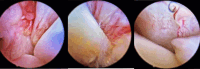
Presentation of case: We report a case of a 28-year-old woman who developed severe pain, swelling, and restricted movement in her left shoulder three weeks postpartum. Septic arthritis due to multi-drug resistant Kingella kingae was diagnosed via PCR analysis of the synovial fluid. The patient was successfully managed with intravenous antibiotics and arthroscopic drainage.
Discussion: This case represents a rare instance of postpartum septic arthritis of the shoulder caused by Kingella kingae. The unusual presentation highlights the importance of considering septic arthritis in postpartum women presenting with shoulder pain, even without typical risk factors. The multi-drug resistance observed in this strain underscores the necessity for comprehensive antibiotic susceptibility testing and individualized treatment strategies.
Conclusion: This case demonstrates that successful management of postpartum septic arthritis caused by Kingella kingae can be achieved through early diagnosis, targeted antibiotic therapy, and minimally invasive surgical intervention. It emphasizes the importance of a multidisciplinary approach, thorough diagnostic evaluation, and heightened clinical suspicion in postpartum women with shoulder pain to prevent long-term complications.
Keywords: Arthroscopy; Kingella kingae; Post-partum; Septic arthritis; Shoulder.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Native joint septic arthritis due to Kingella kingae in an adult.IDCases. 2021 Mar 31;24:e01106. doi: 10.1016/j.idcr.2021.e01106. eCollection 2021. IDCases. 2021. PMID: 33889495 Free PMC article.
-
Primary Septic Arthritis Among Children 6 to 48 Months of Age: Implications for PCR Acquisition and Empiric Antimicrobial Selection.J Pediatr Orthop. 2021 Mar 1;41(3):190-196. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000001744. J Pediatr Orthop. 2021. PMID: 33417393
-
Kingella kingae septic arthritis.Bone Joint J. 2021 Mar;103-B(3):584-588. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.103B3.BJJ-2020-0800.R1. Bone Joint J. 2021. PMID: 33641413
-
Kingella kingae Osteoarticular Infections Approached through the Prism of the Pediatric Orthopedist.Microorganisms. 2021 Dec 24;10(1):25. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10010025. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 35056474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of septic arthritis of the hip in children.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2025 Feb;111(1S):104064. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2024.104064. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 39581493 Review.
Cited by
-
Commentary on "Rare case of postpartum septic arthritis of the shoulder caused by multi-drug resistant Kingella kingae: A case report".Int J Surg Case Rep. 2025 Feb;127:110994. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2025.110994. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 39893964 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Momodu I.I., Savaliya V. StatPearls [Internet] StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island (FL): 2024. Septic arthritis.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538176/ [cité 17 août 2024]. Disponible sur:
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

