A N7-methylguanosine modified circular RNA, circIPP2A2, promotes malignant behaviors in hepatocellular carcinoma by serving as a scaffold in modulating the Hornerin/PI3K/AKT/GSK3β axis
- PMID: 39616161
- PMCID: PMC11608253
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-024-07248-7
A N7-methylguanosine modified circular RNA, circIPP2A2, promotes malignant behaviors in hepatocellular carcinoma by serving as a scaffold in modulating the Hornerin/PI3K/AKT/GSK3β axis
Abstract
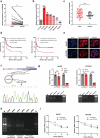
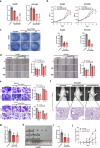
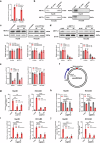
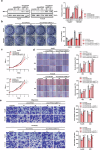
Despite the advancements in treatment strategies, the long-term survival of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is still pessimistic. Therefore, understanding the mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma may offer substantial benefits for patients. Our previous research has revealed that Hornerin promoted HCC progression by regulating the AKT signaling pathway. To investigate the upstream regulatory mechanism, the results from RNA Immunoprecipitation and RNA pull-down indicated that the specific region of circIPP2A2 interacted with Hornerin. Additionally, patients with circIPP2A2 upregulation exhibited a poorer survival outcome following surgery compared to the cases with downregulated circIPP2A2. After the structure verification of circIPP2A2, loss-of-function studies using a lentiviral vector revealed that circIPP2A2 downregulation significantly inhibited HCC tumorigenesis and progression both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, the m7G-MeRIP results demonstrated significant enrichment of circIPP2A2. Subsequent studies validated that METTL1 influenced the stability of circIPP2A2 and its binding affinity with Hornerin. Immunoprecipitation and immunofluorescence indicated that circIPP2A2 served as a molecular scaffold to facilitate Hornerin to interact with PI3K. In conclusion, our findings reveal that circIPP2A2, regulated by N7-methylguanosine modification, promotes malignant behaviors in HCC by serving as a molecular scaffold in modulating the Hornerin/PI3K/AKT/GSK3β axis. Targeting circIPP2A2 may be a promising therapeutic strategy for patients with HCC.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the ethical committee of Zhujiang Hospital and Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center. Informed consent was obtained from all patients. The animal experimental protocols were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Zhujiang Hospital (LAEC-2023-031). All methods were carried out in accordance with the relevant ethical guidelines and regulations.
Figures



References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Singal AG, Kanwal F, Llovet JM. Global trends in hepatocellular carcinoma epidemiology: implications for screening, prevention, and therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2023;20:864–84. - PubMed
-
- Greten TF, Villanueva A, Korangy F, Ruf B, Yarchoan M, Ma L, et al. Biomarkers for immunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2023;20:780–98. - PubMed
-
- Chen LL. The expanding regulatory mechanisms and cellular functions of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21:475–90. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2024A1515012205/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Guangdong Natural Science Foundation)
- 2023A1515010141/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Guangdong Natural Science Foundation)
- 2021B1515230011/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Guangdong Natural Science Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

