FSCN1 is a Potential Therapeutic Target for Atherosclerosis Revealed by Single-Cell and Bulk RNA Sequencing
- PMID: 39618922
- PMCID: PMC11606163
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S480528
FSCN1 is a Potential Therapeutic Target for Atherosclerosis Revealed by Single-Cell and Bulk RNA Sequencing
Abstract
Background: Atherosclerosis (AS) is the major cause of cardiovascular disease. Using integrated single-cell and bulk RNA sequencing data of atherosclerosis, we aimed to investigate the cell phenotype, intercellular communication, and potential therapeutic target in AS.
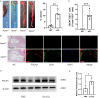
Methods: Single-cell sequencing data from aortic arch of Apoeko mice in normal diet (ND) and high fat diet (HFD) groups (obtained from GSE206239) were analyzed by Seurat, singleR, ReactomeGSA, and cellchat package. scRNA-seq dataset GSE159677 from the carotid artery of the patients with carotid endarterectomy were used to validate the distribution of fascin actin-bundling protein 1 (FSCN1) in cell populations. Bulk RNA sequencing data (GSE43292 and GSE28829) were used to analyzed the expression of FSCN1in AS. A cross-sectional clinical study was utilized to examine the association between FSCN1 and AS. Circulating concentrations of FSCN1 were measured using ELISA kits and assessed using logistic regression analysis and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Apoeko mice fed with HFD and MAECs treated with oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) were established to detect the expression of FSCN1. Furthermore, we knocked down FSCN1 in MAECs to observe its influence on pyroptosis and migration.
Results: The HFD group had a significantly lower percentage of T cells, fibroblasts, and B cells and a significantly higher percentage of monocytes/macrophages cells. Strong interactions between endothelial cell (EC) and fibroblast in ND groups, while EC interactions with smooth muscle cells (SMC) and T cells were stronger in HFD groups. Semaphorin 7 (SEMA7) mediated signaling pathways were enriched in HFD groups and targeted EC driving by SMC. FSCN1was mainly expressed in EC and had a high expression in human AS samples. The cross-sectional study identified that high level of FSCN1 was associated with increased risk of AS. We also observed that high expression of FSCN1 in ox-LDL-induced MAECs and Apoeko mice fed with HFD. Knockdown of FSCN1 reduced pyroptosis and increased the migration in MAECs.
Conclusion: Knockdown of FSCN1 in EC could alleviate the development and progression of AS. FSCN1 may be a potential prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target in AS.
Keywords: FSCN1; atherosclerosis; endothelial cells; migration; pyroptosis.
© 2024 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures






References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

