Evaluation of the osteoarthritis disease burden in China from 1990 to 2021: based on the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021
- PMID: 39618954
- PMCID: PMC11604587
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1478710
Evaluation of the osteoarthritis disease burden in China from 1990 to 2021: based on the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to understand the current status and trend of the disease burden of osteoarthritis (OA) in people over 30 years old in China from 1990 to 2021 and identify the priority population groups, to provide reference data for the prevention and treatment of OA in China.
Methods: The Global Burden of Disease Study 2021 was used to describe the incidence, prevalence, and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) of OA in adult aged 30 years or older in China by sex and age groups, which was used to analyze the disease burden of OA from 1990 to 2021. The joinpoint regression model and age-period-cohort model were used to characterize the temporal trend.
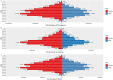
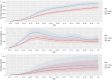
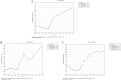
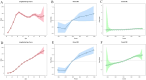
Results: In 2021, the number of OA prevalence in China was about 152.85 million, and the number of incidences was about 11.65 million. The age-standardized prevalence rate (ASPR), age-standardized incidence rate (ASIR) and age-standardized DALYs rate (ASDR) of OA in China are lower than those in developed countries such as Korea, the United States of America and Japan, but higher than those in India. Knee osteoarthritis had the highest ASPR and ASDR. The highest incidence rate was 50-54 years, and the highest prevalence and DALYs rate were in the age group of patients over 95 years old. The incidence rate of women in all age groups is higher than that of men. From 1990 to 2021, the ASIR, ASPR and ASDR of OA in China roughly showed an increasing trend year by year. The age-period-cohort analysis showed that the peak age groups for longitudinal age incidence of OA in China from 1992 to 2021 were 50-54 years and 80-84 years. We found that the OA incidence was highest in the period 2017-2021.
Conclusion: The disease burden of OA in those over 30 years old in China from 1990 to 2021 will become more and more serious, and the target population for primary prevention is the female population under 50 years old. The development of a scientific and effective comprehensive prevention and treatment program for OA is imminent.
Keywords: China; Global Burden of Disease Study; disability-adjusted life years; incidence; osteoarthritis; prevalence.
Copyright © 2024 Liang, Wang, Yu, Jiang, Zhang and Tian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Petersen KK, Drewes AM, Olesen AE, Ammitzbøll N, Bertoli D, Brock C, et al. . The effect of duloxetine on mechanistic pain profiles, cognitive factors and clinical pain in patients with painful knee osteoarthritis-a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study. Eur J Pain. (2022) 26:1650–64. doi: 10.1002/ejp.1988, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

