Immunoglobulin G4-related pancreatitis presenting as an obstructive pancreatic mass in a Latino male
- PMID: 39619465
- PMCID: PMC11604191
- DOI: 10.4103/jfcm.jfcm_143_24
Immunoglobulin G4-related pancreatitis presenting as an obstructive pancreatic mass in a Latino male
Abstract
Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a localized or diffuse autoimmune fibro-inflammatory condition that can affect any organ. The literature is sparse on IgG4-RD in the Latino population. This is a case report of a Latino male diagnosed with IgG4-related pancreatitis presenting as a mass. Our 40-year-old Latino male patient presented with diarrhea and epigastric discomfort progressing to jaundice and pruritus. He had associated elevations in liver enzymes, antinuclear antibody, and IgG4. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography revealed a lobulated pancreatic head mass with common bile duct (CBD) narrowing. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided biopsy of the pancreas revealed no malignancy, and the patient underwent CBD stenting through endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. The patient demonstrated a favorable response to systemic glucocorticoid therapy with resolution of his symptoms and normalization of his liver function tests. Coronavirus disease-2019 infection during treatment had no impact on the outcomes.
Keywords: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; Latino; immunoglobulin G4; pancreatic mass; pancreatitis.
Copyright: © 2024 Journal of Family and Community Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
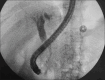
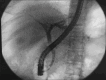
References
-
- Khosroshahi A, Wallace ZS, Crowe JL, Akamizu T, Azumi A, Carruthers MN, et al. International consensus guidance statement on the management and treatment of IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67:1688–99. - PubMed
-
- Brito-Zerón P, Ramos-Casals M, Bosch X, Stone JH. The clinical spectrum of IgG4-related disease. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13:1203–10. - PubMed
-
- Patel NR, Anzalone ML, Buja LM, Elghetany MT. Sudden cardiac death due to coronary artery involvement by IgG4-related disease: A rare, serious complication of a rare disease. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2014;138:833–6. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
