Chinese herbal medicine, Tongxieyaofang, alleviates diarrhea via gut microbiota remodeling: evidence from network pharmacology and full-length 16S rRNA gene sequencing
- PMID: 39619663
- PMCID: PMC11604607
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1502373
Chinese herbal medicine, Tongxieyaofang, alleviates diarrhea via gut microbiota remodeling: evidence from network pharmacology and full-length 16S rRNA gene sequencing
Abstract
Background: Tongxieyaofang (TXYF) was a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) formula for the treatment of diarrhea with liver stagnation and spleen deficiency syndrome, but the potential targets and mechanisms have not been fully clarified. This study aims to explore the potential mechanisms of TXYF in alleviating diarrhea using network pharmacology and full-length 16S rRNA gene sequencing.
Methods: Network pharmacology was applied to identify bioactive compounds and potential targets involved in the role of TXYF in alleviating diarrhea. Meanwhile, a model of diarrhea with liver stagnation and spleen deficiency syndrome was constructed by intragastric administration of Folium senna extract combined with restraint and tail pinch stress. The effect of TXYF on intestinal mucosal microbiota of diarrhea mice was analyzed by full-length 16S rRNA gene sequencing.
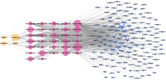
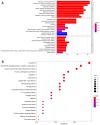
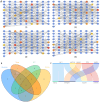
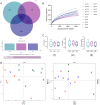
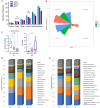
Results: Network pharmacology analysis showed that kaempferol, wogonin, naringenin, and nobiletin were compounds associated with the efficacy of TXYF. TXYF may alleviate diarrhea via multiple BPs and pathways, including TNF signaling pathway, IL-17 signaling pathway, and Toll-like receptor signaling pathway, which are involved in TCM-gut microbiota-host interactions. Then, we found that TXYF administration reshaped the diversity and composition of the intestinal mucosal microbial community of diarrhea mice. Lactobacillus, primarily Lactobacillus johnsonii, was enriched by the administration of TXYF. After TXYF administration, the abundance of Lactobacillus, particularly Lactobacillus johnsonii, was enriched.
Conclusion: Oral administration of TXYF may alleviate diarrhea through remodeling intestinal mucosal microbiota. Promoting the colonization of beneficial commensal bacteria in the intestinal mucosa through gut microbiota-host interactions may be a potential mechanism of TXYF in the treatment of diarrhea.
Keywords: Chinese medicine; Tongxieyaofang (TXYF); diarrhea; full-length 16S rRNA gene sequencing; intestinal mucosal microbiota.
Copyright © 2024 Shao, Wang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
Author HZ was employed by Kangpu Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sishen Pill & Tongxieyaofang ameliorated ulcerative colitis through the activation of HIF-1α acetylation by gut microbiota-derived propionate and butyrate.Phytomedicine. 2025 Jan;136:156264. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156264. Epub 2024 Nov 29. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 39612887
-
Tong-Xie-Yao-Fang strengthens intestinal feedback control of bile acid synthesis to ameliorate irritable bowel syndrome by enhancing bile salt hydrolase-expressing microbiota.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Sep 15;331:118256. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118256. Epub 2024 Apr 25. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38677571
-
Tongxieyaofang Decotion Alleviates IBS by Modulating CHRM3 and Gut Barrier.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Jul 24;18:3191-3208. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S455497. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39081703 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress of traditional Chinese medicine on the treatment of diarrhea by regulating intestinal microbiota and its metabolites based on renal-intestinal axis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Sep 27;14:1483550. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1483550. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39397865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating the biological significance of the TCM principle "promoting urination to regulate bowel movements" through the influence of the intestinal microbiota and their metabolites on the renal-intestinal axis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jan 10;14:1523708. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1523708. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39867340 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated metabolomics and intestinal microbiota analysis to reveal anti-post-weaning diarrhea mechanisms of Modified Yupingfeng Granule in Rex rabbits.Front Microbiol. 2025 Apr 10;16:1470731. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1470731. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40276219 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the effects of Massa Medicata Fermentata with different formulations on the intestinal microbiota and enzyme activities in mice with spleen deficiency constipation.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jan 7;14:1524327. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1524327. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39844840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Sadi R., Nighot P., Nighot M., Haque M., Rawat M., Ma T. Y. (2021). Lactobacillus acidophilus induces a strain-specific and toll-like receptor 2-dependent enhancement of intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier and protection against intestinal inflammation. Am. J. Pathol. 191, 872–884. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2021.02.003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bian Y., Dong Y., Sun J., Sun M., Hou Q., Lai Y., et al. . (2020). Protective effect of kaempferol on LPS-induced inflammation and barrier dysfunction in a coculture model of intestinal epithelial cells and intestinal microvascular endothelial cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 68, 160–167. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b06294 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

