Enhanced biosorption of cadmium ions on immobilized surface-engineered yeast using cadmium-binding peptides
- PMID: 39619698
- PMCID: PMC11604839
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1496843
Enhanced biosorption of cadmium ions on immobilized surface-engineered yeast using cadmium-binding peptides
Abstract
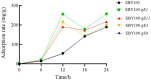
A new type of cadmium (Cd) ion cell surface adsorbent was developed by integrating bacteriophage display peptide library technology with cell surface display technology. Cd2+ chelating resin served as the target molecule in screening experiments, leading to the identification of four Cd2+ -binding peptides. These peptides were introduced into Saccharomyces cerevisiae via the pYD1 plasmid using lithium acetate heat shock transformation. Adsorption efficiency tests indicated that the engineered yeasts adsorbed more Cd2+ than the control strain EBY100 when exposed to the same amount of Cd2+. Among these peptides, sequence 3-containing strain was demonstrated to have the highest Cd2+ adsorption efficiency, being 35% higher than the control strain. Additionally, when this recombinant yeast strain was immobilized using sodium alginate, the adsorption efficiency was increased by 55.7% compared to the control strain.
Keywords: biosorption; cadmium-binding peptide; immobilization; phage peptide library; surface-engineered yeast.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Sun, Wang, Fan, Wang, Liu and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Enhanced Biosorption of Nickel Ions on Immobilized Surface-Engineered Yeast Using Nickel-Binding Peptides.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jun 26;10:1254. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01254. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31297097 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Surface Display of Four Types of Solanum nigrum Metallothionein on Saccharomyces cerevisiae for Biosorption of Cadmium.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016 May 28;26(5):846-53. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1512.12041. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26838339
-
Exopolymeric substances production by Bacillus cereus KMS3-1 enhanced its biosorption efficiency in removing Cd2+ and Pb2+ in single and binary metal mixtures.Environ Res. 2023 Jul 1;228:115917. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.115917. Epub 2023 Apr 14. Environ Res. 2023. PMID: 37062474
-
Process optimization and modeling of Cd2+ biosorption onto the free and immobilized Turbinaria ornata using Box-Behnken experimental design.Sci Rep. 2022 Feb 28;12(1):3256. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-07288-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35228594 Free PMC article.
-
Biosorption of copper, zinc, cadmium and chromium ions from aqueous solution by natural foxtail millet shell.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018 Dec 15;165:61-69. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.08.084. Epub 2018 Sep 4. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018. PMID: 30193165
References
-
- Arsenie T., Cara I. G., Popescu M.-C., Motrescu I., Bulgariu L. (2022). Evaluation of the adsorptive performances of rapeseed waste in the removal of toxic metal ions in aqueous media. Water 14:4108. doi: 10.3390/w14244108 - DOI
-
- Jingshuang H., Chunyan M., Xin T., Yi Zhuolin X., Liu M. C. (2006). Screening of Cd2+ binding peptides and their affinity with heavy metal ions. Microbiol. China 5, 70–74. doi: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.2006.05.016 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

