Influencing Factors Associated with Psychological Capital Among Ischemic Stroke Patients: A Latent Profile Analysis
- PMID: 39619944
- PMCID: PMC11608031
- DOI: 10.2147/PRBM.S482943
Influencing Factors Associated with Psychological Capital Among Ischemic Stroke Patients: A Latent Profile Analysis
Abstract
Background: China has the highest incidence of stroke worldwide because of a high rate of recurrence of ischemic stroke, which has significant negative impacts on the physical and mental health of patients. However, little research has been devoted to the psychological capital of ischemic stroke patients.
Purpose: To investigate the psychological capital of ischemic stroke patients, and uses latent profile analysis to identify the potential profiles of the psychological capital among patients as well as to explore heterogeneity within subgroups and the factors influencing it.
Methods: A survey was distributed among and completed by 427 ischemic stroke patients from November 2023 to March 2024. Four types of questionnaires were administered: the Psychological Capital Questionnaire (PCQ-26), Perceived Stress Scale (CPSS), Athens Insomnia Scale (AIS), and a general information questionnaire.
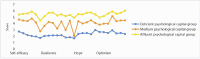
Results: Three latent profiles of the psychological capital of ischemic stroke patients were identified: the deficient psychological capital group(19.7%), medium psychological capital group(52.5%), and affluent psychological capital group(27.9%). Compared with the deficient psychological capital group, the results of a disordered multi-classification logistic regression analysis showed that the factors influencing the participants of the medium psychological capital group were their marital status (married OR = 1.081, 95% CI: 1.163-7.468, p = 0.023), perceived stress (OR = -0.2, 95% CI: 0.769-0.872, p < 0.001), and insomnia (OR = -0.273, 95% CI: 0.696-0.833, p < 0.001). The factors influencing the affluent psychological capital group were perceived stress (OR = -0.334, 95% CI: 0.664-0.773, p < 0.001) and insomnia (OR = -0.46, 95% CI: 0.56-0.712, p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Three potential categories of psychological capital in ischemic stroke patients were identified. Sex, marital status, education, perceived stress, and insomnia were found to be associated with psychological capital in stroke patients. Future research should explore other determinants of psychological capital in ischemic stroke patients to formulate interventions that can improve their psychological capital.
Keywords: insomnia; ischemic stroke; latent profile analysis; perceived stress; psychological capital.
© 2024 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Brief report on stroke prevention treatment in China Writing Group. Brief report on stroke prevention treatment in China, 2021. Chin J Cerebrovasc Dis. 2023;20(11):783–793.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources