Nutritional Benefits of Lycopene and Beta-Carotene: A Comprehensive Overview
- PMID: 39619948
- PMCID: PMC11606860
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.4502
Nutritional Benefits of Lycopene and Beta-Carotene: A Comprehensive Overview
Abstract
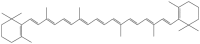
Certain carotene components, such as lycopene and beta-carotene, are found in tomatoes, carrots, sweet potatoes, etc. and are good for human health. It gives plants their distinctive red color. A class of lipid-soluble natural pigments known as carotenoids is the precursor of vitamin A and is vital for antioxidant defense against peroxides in cells and tissues. This review provides an overview of the current state of knowledge and research on the sources, structures, physiochemical properties, absorption and metabolism, functional advantages, and prevention of many diseases associated with lycopene and beta-carotene. These antioxidants have been linked to a lower risk of cardiovascular disease and cancer, and they also help draw pollinators to flowers. Carrots and sweet potatoes are also rich sources of beta-carotene, which strengthens the immune system and improves eye health. The vivid color of many plants reproductive organs, including flowers and fruits, is caused by carotenoid, a secondary metabolite that is produced in plastids. The distinctive red color and many other health advantages are attributed to lycopene. When ingested through food or supplements, lycopene and beta-carotene help manage and prevent a number of diseases, including cancer, metabolic, inflammatory, cardiovascular, hepatic, ophthalmic, skeletal, and infertility disorders. The main point is that toxicity is uncommon, and these carotenoids are generally accepted to be safe at different doses. Including these nutrients in your diet can improve your general health and provide illness prevention.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Beta‐carotene; Carotenoid; Health Benefits; Lycopene.
© 2024 The Author(s). Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Abd Al Haleem, E. N. , Ahmed H. I., and El‐Naga R. N.. 2023. “Lycopene and Chrysin Through Mitigation of Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress Exerted Antidepressant Effects in Clonidine‐Induced Depression‐Like Behavior in Rats.” Journal of Dietary Supplements 20, no. 3: 391–410. - PubMed
-
- Abdel‐Naim, A. B. , Hassanein E. H., Binmahfouz L. S., et al. 2023. “Lycopene Attenuates Chlorpyrifos‐Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats via Activation of Nrf2/HO‐1 Axis.” Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 262: 115122. - PubMed
-
- Aboubakr, M. , Elbadawy M., Ibrahim S. S., et al. 2023. “Allicin and Lycopene Possesses a Protective Effect Against Methotrexate‐Induced Testicular Toxicity in Rats.” Pakistan Veterinary Journal 43, no. 3: 559–566.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

