Long-term exposure of sucralose induces neuroinflammation and ferroptosis in human microglia cells via SIRT1/NLRP3/IL-1β/GPx4 signaling pathways
- PMID: 39619997
- PMCID: PMC11606902
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.4488
Long-term exposure of sucralose induces neuroinflammation and ferroptosis in human microglia cells via SIRT1/NLRP3/IL-1β/GPx4 signaling pathways
Abstract
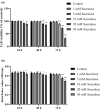
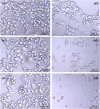
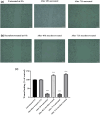
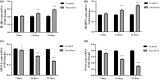
Microglia serve as the primary defense mechanism in the brain. Artificial sweeteners are widely used as dietary supplements, though their long-term effects remain uncertain. In this study, we investigated the effects of sucralose on microglia during prolonged exposure via the neuroinflammatory and ferroptosis pathways. Initially, human microglial clone 3 (HMC3) cells were exposed to sucralose (0-50 mM) for 24, 48, and 72 h to investigate the short-term effects. Subsequently, HMC3 cells were treated with 1 mM sucralose for 7, 14, and 21 days to examine long-term effects. We measured levels of interleukin-1β (IL-1β), NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3), 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine (8-OHdG), Sirtuin-1 (SIRT1), glutathione peroxidase-4 (GPx4), reduced glutathione (GSH), malondialdehyde (MDA), ferrous iron (Fe2+), and caspase 3/7. Additionally, we analyzed the impact of sucralose on cell morphology, migration, and expression levels of IL-1β, NLRP3, SIRT1, and GPx4. Sucralose inhibited cell viability and proliferation in HMC3 cells in a concentration- and time-dependent manner and induced membrane and nuclear abnormalities. Moreover, sucralose significantly reduced the cell migration rate. Long-term sucralose treatment decreased Fe2+, GPx4, GSH, and SIRT1 levels in HMC3 cells while increasing IL-1β, MDA, NLRP3, 8-OHdG, and caspase 3/7 activity. Sucralose treatment also enhanced microglial activation and neuroinflammation by upregulating IL-1β and NLRP3 and downregulating SIRT1 and GPx4, thereby inducing ferroptosis and suppressing cell viability. Consequently, high concentrations or long-term sucralose treatment may induce neuroinflammation and ferroptosis by targeting the SIRT1/NLRP3/IL-1β/GPx4 pathway in HMC3 cells.
Keywords: NLRP3; artificial sweeteners; ferroptosis; microglia; neuroinflammation; sirtuins; sucralose.
© 2024 The Author(s). Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Silent information regulator sirtuin 1 ameliorates acute liver failure via the p53/glutathione peroxidase 4/gasdermin D axis.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Mar 21;30(11):1588-1608. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i11.1588. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38617450 Free PMC article.
-
Gandouling Regulates Ferroptosis and Improves Neuroinflammation in Wilson's Disease Through the LCN2/NLRP3 Signaling Pathway.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Aug 23;17:5599-5618. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S465341. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39193124 Free PMC article.
-
Gastrodin alleviates cisplatin nephrotoxicity by inhibiting ferroptosis via the SIRT1/FOXO3A/GPX4 signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jan 30;319(Pt 3):117282. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117282. Epub 2023 Oct 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37802374
-
NLRP3 inflammasome deficiency attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting ferroptosis.Brain Res Bull. 2023 Feb;193:37-46. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2022.11.016. Epub 2022 Nov 23. Brain Res Bull. 2023. PMID: 36435361
-
Nicotinamide mononucleotide mitigates neuroinflammation by enhancing GPX4-mediated ferroptosis defense in microglia.Brain Res. 2024 Dec 15;1845:149197. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2024.149197. Epub 2024 Aug 30. Brain Res. 2024. PMID: 39216693
Cited by
-
Sucralose: A Review of Environmental, Oxidative and Genomic Stress.Nutrients. 2025 Jul 1;17(13):2199. doi: 10.3390/nu17132199. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40647303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aspartame and ischemic stroke: unraveling the molecular link through network toxicology and molecular docking analysis.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 4;15(1):23871. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-08898-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40615604 Free PMC article.
-
Potential role of SIRT1 in cell ferroptosis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Mar 5;13:1525294. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1525294. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40109363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Crosstalk Between Ferritinophagy and Ferroptosis in Ischemic Stroke: Regulatory Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jul 20;45(1):73. doi: 10.1007/s10571-025-01593-7. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40684405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NLRP3 inflammasome as a therapeutic target in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: role of phytochemicals.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 17;16:1567312. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1567312. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40313623 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abou‐Donia, M. B. , El‐Masry, E. M. , Abdel‐Rahman, A. A. , McLendon, R. E. , & Schiffman, S. S. (2008). Splenda alters gut microflora and increases intestinal p‐glycoprotein and cytochrome p‐450 in male rats. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health. Part A, 71(21), 1415–1429. 10.1080/15287390802328630 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

