A micro-CT study of the pulp cavity morphology of maxillary fourth premolar teeth in dogs
- PMID: 39620112
- PMCID: PMC11605712
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1499465
A micro-CT study of the pulp cavity morphology of maxillary fourth premolar teeth in dogs
Abstract
Introduction: The objectives of the present study were (1) to describe the anatomy of the endodontic system of the dog's maxillary fourth premolar tooth (MxPM4) in relation to the morphology of the crown, (2) to determine if variations of the endodontic system exist, and (3) to look at the implications for endodontic treatment.
Methods: Ten MxPM4 were harvested en bloc and scanned using micro-computed tomography (micro-CT).
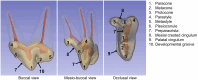
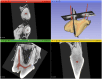
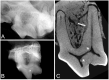
Results: The morphology of the pulp chamber mostly corresponded with the shape of the crown. Three pulp horns were clearly visible and related to the paracone, the metacone, and the metastyle. Nevertheless, the pulp horns of the metacone and metastyle could be fused, partially fused or distinct. Other pulp projections were also present, but rarely, in the parastyle, the protocone, and the plesioconule. All teeth showed a noticeable angulation of an average of 150 degrees at the coronal third of the mesiopalatal canal.
Discussion: Thus, the most common transcoronal approach for root canal treatment does not allow a straight access to the apex. There were also minor variations in the locations of the canal orifices. This first micro-CT study of the MxPM4 in dogs showed anatomical features and variations of the pulp cavity that have not been described before.
Keywords: dog; endodontic; maxillary fourth premolar teeth; micro-CT; pulp cavity; root canal treatment (RCT).
Copyright © 2024 Morin and D'Astous.
Conflict of interest statement
M-CM and JD’A were employed by company Centre Vétérinaire Daubigny. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Lobprise HB, Dodd JR. Wiggs's Veterinary Dentistry: Principles and Practice. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons; (2019). p. 544.
-
- Versiani MA, Basrani B, Sousa-Neto A. The Root Canal Anatomy in Permanent Dentition. Cham: Springer International Publishing; (2019). p. 19.
-
- Berman LH, Hargreaves KM. Cohen's Pathways of the Pulp. St-Louis, MO: Elsevier; (2020).
-
- Gracis M. Dental anatomy and physiology. In: BSAVA manual of canine and feline dentistry and oral surgery. Quedgeley, Gloucs: British Small Animal Veterinary Association; (2018). p. 6–32.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

