Targeting regulated cell death pathways in cancers for effective treatment: a comprehensive review
- PMID: 39620145
- PMCID: PMC11604647
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1462339
Targeting regulated cell death pathways in cancers for effective treatment: a comprehensive review
Abstract
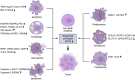
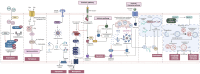
Cancer is a complex disease characterized by specific "mission-critical" events that drive the uncontrolled growth and spread of tumor cells and their offspring. These events are essential for the advancement of the disease. One of the main contributors to these events is dysregulation of cell death pathways-such as apoptosis, necroptosis, ferroptosis, autophagy, pyroptosis, cuproptosis, parthanatos and-allows cancer cells to avoid programmed cell death and continue proliferating unabated. The different cell death pathways in cancers provide useful targets for cancer treatment. This review examines recent progresses in the preclinical and clinical development of targeting dysregulated cell death pathways for cancer treatment. To develop effective cancer therapies, it is essential to identify and target these mission-critical events that prevent tumor cells from timely death. By precisely targeting these crucial events, researchers can develop therapies with maximum impact and minimal side effects. A comprehensive understanding of the molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying these regulated cell death pathways will further the development of highly effective and personalized cancer treatments.
Keywords: apoptosis; autophagy; cancer therapy; cuproptosis; ferroptosis; necroptosis; pyroptosis; regulated cell death pathway.
Copyright © 2024 Saxena, Welsh and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
-
- Akhtar F., Bokhari S. R. A. (2024). Apoptosis. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

