Locus-specific differential expression of human satellite sequences in the nuclei of cancer cells and heat-shocked cells
- PMID: 39620275
- PMCID: PMC11622622
- DOI: 10.1080/19491034.2024.2431239
Locus-specific differential expression of human satellite sequences in the nuclei of cancer cells and heat-shocked cells
Erratum in
-
Correction.Nucleus. 2025 Dec;16(1):2443274. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2024.2443274. Epub 2025 Jan 21. Nucleus. 2025. PMID: 39835659 No abstract available.
Abstract
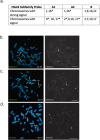
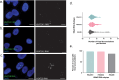
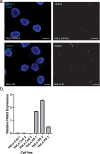
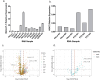
Human satellitess(HSats) are pericentric, tandemly repeating satellite DNA sequences in the human genome. While silent in normal cells, a subset of HSat2 noncoding RNA is expressed and accumulates in the nucleus of cancer cells. We developed a FISH-based approach for identification of the distribution of three subfamilies of HSat2 (A1, A2, B) sequences on individual human chromosomes. Further, using the HSat subfamily annotations in the T2T completed centromere satellite (CenSat) sequence, we isolated, defined and mapped differentially expressed sequence variants of nuclear-restricted HSat2 and HSat3 RNA from cancer cell lines and heat-shocked cells. We identified chromosome-specific and subfamily-specific expression of HSat2 and HSat3 and established a computational pipeline for differential expression analysis of tandemly repeated satellite sequences. Results suggest the differential expression of chromosome-specific HSat2 arrays in the human genome may underlie their accumulation in cancer cells and that specific HSat3 loci are upregulated upon heat shock.
Keywords: Cancer; RNA-seq; Satellite DNA; centromere; heat shock; nucleus; pericentromere; repetitive DNA.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Heat shock factor 1 binds to and transcribes satellite II and III sequences at several pericentromeric regions in heat-shocked cells.Exp Cell Res. 2010 Jul 1;316(11):1845-55. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.02.002. Epub 2010 Feb 10. Exp Cell Res. 2010. PMID: 20152833
-
Overexpression of Pericentromeric HSAT2 DNA Increases Expression of EMT Markers in Human Epithelial Cancer Cell Lines.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 7;24(8):6918. doi: 10.3390/ijms24086918. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108080 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome-specific alpha-satellite DNA from the centromere of chimpanzee chromosome 4.Chromosoma. 1997 Sep;106(4):226-32. doi: 10.1007/s004120050243. Chromosoma. 1997. PMID: 9254724
-
A classical revival: Human satellite DNAs enter the genomics era.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Aug;128:2-14. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.04.012. Epub 2022 Apr 27. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35487859 Review.
-
Satellite RNAs: emerging players in subnuclear architecture and gene regulation.EMBO J. 2023 Sep 18;42(18):e114331. doi: 10.15252/embj.2023114331. Epub 2023 Aug 1. EMBO J. 2023. PMID: 37526230 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Noncoding RNAs in nuclear organization.Nucleus. 2025 Dec;16(1):2477848. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2025.2477848. Epub 2025 Mar 13. Nucleus. 2025. PMID: 40083045 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
