MRgFUS subthalamotomy in Parkinson's disease: an approach aimed at minimizing Lesion Volume
- PMID: 39622797
- PMCID: PMC11612194
- DOI: 10.1038/s41531-024-00843-7
MRgFUS subthalamotomy in Parkinson's disease: an approach aimed at minimizing Lesion Volume
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: MRgFUS subthalamotomy in Parkinson's disease: an approach aimed at minimizing Lesion Volume.NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2025 Jan 30;11(1):26. doi: 10.1038/s41531-025-00871-x. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2025. PMID: 39885174 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
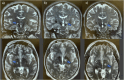
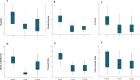
Idiopathic Parkinson's Disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, and postural instability. Magnetic Resonance-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound (MRgFUS) of the subthalamic nucleus (STN) is gaining recognition as a minimally invasive surgical option. This study assesses the safety and efficacy of unilateral MRgFUS subthalamotomy, aiming to create the smallest effective lesion. Between June 2021 and October 2023, twelve PD patients underwent the procedure, with primary outcomes focused on safety and motor improvements after six months. Results indicated significant motor improvements, with over 50% reduction in tremor, rigidity, and bradykinesia, while balance and gait remained stable. Quality of life also improved. Side effects were generally mild and transient, though some patients experienced involuntary movements, managed through medication adjustments. Despite limitations, this technique appears to offer a promising, less-invasive alternative for managing PD symptoms with a favorable risk-benefit profile. Further research is necessary to refine the procedure and assess long-term outcomes.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Fry W. J., Mosberg W. H., Fry F. J. Production of focal destructive lesions in the central nervous system with ultrasound*. 336 (1954). - PubMed
-
- Meyers, R. et al. Early experiences with ultrasonic irradiation of the pallido fugal and nigral complexes in hyperkinetic and hypertonic disorders *. (1958). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

