Reimbursement in the age of generalist radiology artificial intelligence
- PMID: 39622981
- PMCID: PMC11612271
- DOI: 10.1038/s41746-024-01352-w
Reimbursement in the age of generalist radiology artificial intelligence
Abstract
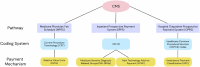
We argue that generalist radiology artificial intelligence (GRAI) challenges current healthcare reimbursement frameworks. Unlike narrow AI tools, GRAI's multi-task capabilities render existing pathways inadequate. This perspective examines key questions surrounding GRAI reimbursement, including issues of coding, valuation, and coverage policies. We aim to catalyze dialogue among stakeholders about how reimbursement might evolve to accommodate GRAI, potentially influencing AI reimbursement strategies in radiology and beyond.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: P.R. is co-founder of a2z Radiology AI. S.D. is a part-time employee of a2z Radiology AI.
Figures

References
-
- Zhou, H.-Y., Adithan, S., Acosta, J. N., Topol, E. J. & Rajpurkar, P. A Generalist Learner for Multifaceted Medical Image Interpretation. arXiv [cs.CV] (2024).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

