Contamination characteristics of heavy metals and enrichment capacity of native plants in soils around typical coal mining areas in Gansu, China
- PMID: 39622997
- PMCID: PMC11612137
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-81740-0
Contamination characteristics of heavy metals and enrichment capacity of native plants in soils around typical coal mining areas in Gansu, China
Abstract
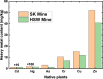
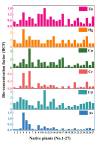
Exploitation of mineral resources is a vital backbone of a country's socio-economic development. However, the coal exploration would cause ecological and environmental problems such as pollutions of water, soils and atmosphere. Especially, the pollution of heavy metals of soil has become increasingly severity. Plant enrichment and tolerance to heavy metals are crucial for the phytoremediation of coal gangue mountain. In phytoremediation, phytostabilization which can reduce the metal contamination of soil by uptake and burn-off of heavy metals with highly accumulating plants, is one of the most effective techniques of eco-remediation treatment. In present work, heavy metals contamination of soil and plants in the Yaojie mining which located in arid and semi-arid area of northwest China were investigated through field investigation. To identify the suitable plants for the remediation and ecological reclamation of heavy metal contaminated soil in typical mining area, the contamination characteristics of heavy metals in the above-ground parts of 27 native plants and their surrounding non-rhizosphere soils were analyzed. After eliminated by wet digestion and high-pressure closed digestion, the mass fractions of Zinc (Zn), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr) and copper (Cu) were determined with inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer, and the contents of Hydrargyrum (Hg) and Arsenic (As) were analyzed with atomic fluorescence spectrophotometer. The Nemerow pollution index showed that in the surrounding soil, the pollution index of heavy metal was 6.32, which reached the extreme severe pollution level. Among the 6 heavy metals, the most severe contamination being Hg (Pi = 8.50) and had particularly strong Coefficient of variation (CV = 105.8%), which is more likely to be caused by anthropogenic activities. In the aboveground parts of 27 plants, except for Zn, other metals exceeded the standard level, and the exceedance rates in descending order were As, Hg, Cr, Cd, and Cu. The most severe exceedance of As was found in C. virgata, which was as high as 19.20, and the average exceedance rate of As in all plants was 2.79. Bioconcentration Factor (BCF) was utilized as an indicator of the enrichments of various metals in 27 plants. The maximum value of BCF for As and Hg in C. virgata were 1.52 and 2.50, Cr and Cu in X. sibiricum were 0.72 and 2.32, Cd and Zn in S. glauca were 3.33 and 1.82. As revealed, except Cr, all the BCF of other metals are greater than 1, indicating that the three plants exhibited a strong accumulation capacity of heavy metal and are potential candidate pioneer species for the removal of heavy metals from the contaminated soil in the Yaojie mining area. This study provides a basis for plant selection for ecological restoration of contaminated soils in arid and semi-arid regions.
Keywords: Ecological restoration; Enrichment capacity; Heavy metals pollution; Native plants; Phytoremediation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
[Accumulation Characteristics, Pollution Risk, and Source Analysis of Soil Heavy Metals Around a Coal Mining Area in the Baiyin Section of the Upper Yellow River].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2025 Apr 8;46(4):2475-2485. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202404060. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2025. PMID: 40230152 Chinese.
-
Exploring the accumulation capacity of dominant plants based on soil heavy metals forms and assessing heavy metals contamination characteristics near gold tailings ponds.J Environ Manage. 2024 Feb;351:119838. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.119838. Epub 2023 Dec 24. J Environ Manage. 2024. PMID: 38145590
-
Study on remediation capacity of typical forage grasses for Cu, Pb, and Cd contamination in coal gangue-accumulated soils.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2025 Jul 1;299:118404. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2025.118404. Epub 2025 May 27. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2025. PMID: 40424729
-
An integrated overview of metals contamination, source-specific risks investigation in coal mining vicinity soils.Environ Geochem Health. 2023 Nov;45(11):7425-7458. doi: 10.1007/s10653-023-01672-y. Epub 2023 Jul 14. Environ Geochem Health. 2023. PMID: 37452259 Review.
-
Major influencing factors identification and probabilistic health risk assessment of soil potentially toxic elements pollution in coal and metal mines across China: A systematic review.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024 Apr 1;274:116231. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.116231. Epub 2024 Mar 19. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024. PMID: 38503102
Cited by
-
Evaluation and Source Analysis of Plant Heavy Metal Pollution in Kalamaili Mountain Nature Reserve.Plants (Basel). 2025 May 19;14(10):1521. doi: 10.3390/plants14101521. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40431086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang, L., Zhang, Y. X., Song, B., Wu, Y. & Zhou, Y. Y. Heavy metal enrichment characteristics and application potential of dominant plants in the lead-zinc mining area of Lanping, Yunnan. J. Environ. Sci.41(09), 4210–4217. 10.13227/j.hjkx.202001019 (2020).
-
- Zhu, Y., An, Y. F., Li, X. Y., Cheng, L. & Lv, S. J. Geochemical characteristics and health risks of heavy metals in agricultural soils and crops from a coal mining area in Anhui province, China. Environ. Res.241, 117670. 10.1016/j.envres.2023.117670 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Khan, S. R., Singh, P. C., Schmettow, M., Singh, S. K. & Rastogi, N. Exploring the influence of ground-dwelling ant bioturbation activity on physico-chemical, biological properties and heavy metal pollution in coal mine spoil. Pedobiologia104, 150960. 10.1016/j.pedobi.2024.150960 (2024).
-
- Ustaoglu, F. et al. Appraisal of macro elements and trace metals in the edible fish from the Black Sea connecting coastal river, Türkiye: A preliminary study for health risk assessment. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci.71, 103406. 10.1016/j.rsma.2024.103406 (2024).
-
- Liu, L., Wang, J. I., Zhai, J. R., Yan, D. P. & Lin, Z. D. Regional disparities and technological approaches in heavy metal remediation: A comprehensive analysis of soil contamination in Asia. Chemosphere366, 143485. 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2024.143485 (2024). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

