Extreme wrinkling of the nuclear lamina is a morphological marker of cancer
- PMID: 39623008
- PMCID: PMC11612457
- DOI: 10.1038/s41698-024-00775-8
Extreme wrinkling of the nuclear lamina is a morphological marker of cancer
Abstract
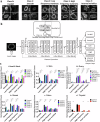
Nuclear atypia is a hallmark of cancer. A recent model posits that excess surface area, visible as folds/wrinkles in the lamina of a rounded nucleus, allows the nucleus to take on diverse shapes with little mechanical resistance. Whether this model is applicable to normal and cancer nuclei in human tissues is unclear. We image nuclear lamins in patient tissues and find: (a) nuclear laminar wrinkles are present in control and cancer tissue but are obscured in hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) images, (b) nuclei rarely have a smooth lamina, and (c) wrinkled nuclei assume diverse shapes. Deep learning reveals the presence of extreme nuclear laminar wrinkling in cancer tissues, which is confirmed by Fourier analysis. These data support a model in which excess surface area in the nuclear lamina enables nuclear shape diversity in vivo. Extreme laminar wrinkling is a marker of cancer, and imaging the lamina may benefit cancer diagnosis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: VCS is a consultant and equity holder for Femtovox Inc (unrelated to current work). TCW, CRD, SM, HP, SA, IS, VT, DGR, SC, and TPL declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Beale, L. Examination of sputum from a case of cancer of the pharynx and the adjacent parts. Arch. Med2, 1860–1861 (1860).
-
- Krishnamurti, U. G., Fitzgibbons, P. L., Connolly, J. L. Protocol for the Examination of Resection Specimens from Patients with Invasive Carcinoma of the Breast, https://www.cap.org/protocols-and-guidelines/cancer-reporting-tools/canc... (2023).
-
- Fitzgibbons, P. L., Connolly, J. L. Protocol for the Examination of Biopsy Specimens from Patients with Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS) of the Breasthttps://www.cap.org/protocols-and-guidelines/cancer-reporting-tools/canc... (2021). - PubMed
-
- Mete, O. Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Carcinomas of the Thyroid Glan, https://www.cap.org/protocols-and-guidelines/cancer-reporting-tools/canc... (2023).
-
- Seethala, R. R. Protocol for the Examination of Specimens from Patients with Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck, https://www.cap.org/protocols-and-guidelines/cancer-reporting-tools/canc... (2022).
Grants and funding
- I01 CX002776/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- RR200043/Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (Cancer Prevention Research Institute of Texas)
- 1I01CX002776/U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (Department of Veterans Affairs)
- U01 CA225566/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DE032344/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

