Mitochondrial calcium uniporter complex controls T-cell-mediated immune responses
- PMID: 39623165
- PMCID: PMC11772621
- DOI: 10.1038/s44319-024-00313-4
Mitochondrial calcium uniporter complex controls T-cell-mediated immune responses
Abstract
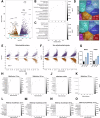
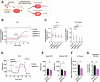
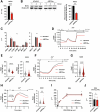
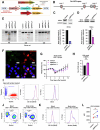
T-cell receptor (TCR)-induced Ca2+ signals are essential for T-cell activation and function. In this context, mitochondria play an important role and take up Ca2+ to support elevated bioenergetic demands. However, the functional relevance of the mitochondrial-Ca2+-uniporter (MCU) complex in T-cells was not fully understood. Here, we demonstrate that TCR activation causes rapid mitochondrial Ca2+ (mCa2+) uptake in primary naive and effector human CD4+ T-cells. Compared to naive T-cells, effector T-cells display elevated mCa2+ and increased bioenergetic and metabolic output. Transcriptome and proteome analyses reveal molecular determinants involved in the TCR-induced functional reprogramming and identify signalling pathways and cellular functions regulated by MCU. Knockdown of MCUa (MCUaKD), diminishes mCa2+ uptake, mitochondrial respiration and ATP production, as well as T-cell migration and cytokine secretion. Moreover, MCUaKD in rat CD4+ T-cells suppresses autoimmune responses in an experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) multiple sclerosis model. In summary, we demonstrate that mCa2+ uptake through MCU is essential for proper T-cell function and has a crucial role in autoimmunity. T-cell specific MCU inhibition is thus a potential tool for targeting autoimmune disorders.
Keywords: Autoimmunity; Calcium; MCU; Mitochondria; T-cell.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and competing interests statement. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Ben-Nun A, Wekerle H, Cohen IR (1981) The rapid isolation of clonable antigen-specific T lymphocyte lines capable of mediating autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Eur J Immunol 11:195–199 - PubMed
-
- Berod L, Friedrich C, Nandan A, Freitag J, Hagemann S, Harmrolfs K, Sandouk A, Hesse C, Castro CN, Bähre H et al (2014) De novo fatty acid synthesis controls the fate between regulatory T and T helper 17 cells. Nat Med 20:1327–1333 - PubMed
-
- Berthold MR, Cebron N, Dill F, Gabriel TR, Kötter T, Meinl T, Ohl P, Thiel K, Wiswedel B (2009) KNIME - the Konstanz information miner: version 2.0 and beyond. SIGKDD Explor Newsl 11:26–31
-
- Bogeski I, Kummerow C, Al-Ansary D, Schwarz EC, Koehler R, Kozai D, Takahashi N, Peinelt C, Griesemer D, Bozem M et al (2010) Differential redox regulation of ORAI ion channels: a mechanism to tune cellular calcium signaling. Sci Signal 3:ra24 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- SFB1190 P17/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
- SFB1027 C4/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
- IRTG1816/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
- RI2150/5-1 435235019/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
- RI2150/2-2 251546152/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
- RTG2550/1 411422114/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
- SFB1218 269925409/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
- SFB1328 A01 335447717/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
- SFB TRR 274/1 A03 408885537/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
- SFB1190 P13/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
- 101021345/European Commission (EC)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

