Engineering extracellular vesicles to transiently permeabilize the blood-brain barrier
- PMID: 39623431
- PMCID: PMC11613868
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-024-03019-w
Engineering extracellular vesicles to transiently permeabilize the blood-brain barrier
Abstract
Background: Drug delivery to the brain is challenging due to the restrict permeability of the blood brain barrier (BBB). Recent studies indicate that BBB permeability increases over time during physiological aging likely due to factors (including extracellular vesicles (EVs)) that exist in the bloodstream. Therefore, inspiration can be taken from aging to develop new strategies for the transient opening of the BBB for drug delivery to the brain.
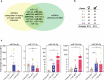
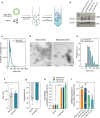
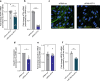
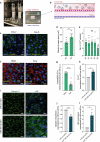
Results: Here, we evaluated the impact of small EVs (sEVs) enriched with microRNAs (miRNAs) overexpressed during aging, with the capacity to interfere transiently with the BBB. Initially, we investigated whether the miRNAs were overexpressed in sEVs collected from plasma of aged individuals. Next, we evaluated the opening properties of the miRNA-enriched sEVs in a static or dynamic (under flow) human in vitro BBB model. Our results showed that miR-383-3p-enriched sEVs significantly increased BBB permeability in a reversible manner by decreasing the expression of claudin 5, an important tight junction protein of brain endothelial cells (BECs) of the BBB, mediated in part by the knockdown of activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4).
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that engineered sEVs have potential as a strategy for the temporary BBB opening, making it easier for drugs to reach the brain when injected into the bloodstream.
Keywords: Blood–brain barrier; Claudin 5; Extracellular vesicles; MicroRNA; Microfluidic system; Modulation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The collection of umbilical cord blood (UCB) was approved by the ethical committee of Dr. Daniel de Matos Maternity Hospital in Coimbra (protocol HUC-01-11), Portugal. The collection of adult blood was approved by the Faculty of Medicine of the University of Coimbra and the Portuguese Institute for Blood and Transplantation (IPST) in the facilities of Blood and Transplantation Center of Coimbra (CSTC) (protocol: CE-088/2020). All the donors of the UCB and adult blood signed an informed consent form, in compliance with the Portuguese legislation. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Engelhardt B, Sorokin L. The blood–brain and the blood–cerebrospinal fluid barriers: function and dysfunction. Semin Immunopathol. 2009;31(4):497–511. - PubMed
-
- Cui Y, et al. Brain endothelial PTEN/AKT/NEDD4-2/MFSD2A axis regulates blood-brain barrier permeability. Cell Rep. 2021;36(1): 109327. - PubMed
-
- Oldendorf WH, Brown WJ. Greater number of capillary endothelial cell mitochondria in brain than in muscle. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975;149(3):736–8. - PubMed
-
- Lipinski CA. Drug-like properties and the causes of poor solubility and poor permeability. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2000;44(1):235–49. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 764958/Horizon 2020 Framework Programme
- 764958/Horizon 2020 Framework Programme
- 764958/Horizon 2020 Framework Programme
- 764958/Horizon 2020 Framework Programme
- 764958/Horizon 2020 Framework Programme
- 764958/Horizon 2020 Framework Programme
- 952266/European Unions Horizon 2020
- 952266/European Unions Horizon 2020
- 952266/European Unions Horizon 2020
- 952266/European Unions Horizon 2020
- 952266/European Unions Horizon 2020
- 952266/European Unions Horizon 2020
- PTDC/BTM-SAL/5174/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia
- PTDC/BTM-SAL/5174/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia
- PTDC/BTM-SAL/5174/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia
- PTDC/BTM-SAL/5174/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia
- PTDC/BTM-SAL/5174/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia
- PTDC/BTM-SAL/5174/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia
- PTDC/BTM-SAL/5174/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia
- 02/C05-i01.01/2022.PC644937233-00000047/Plano de Recuperação e Resiliência, Portugal
- 02/C05-i01.01/2022.PC644937233-00000047/Plano de Recuperação e Resiliência, Portugal
- 02/C05-i01.01/2022.PC644937233-00000047/Plano de Recuperação e Resiliência, Portugal
- 02/C05-i01.01/2022.PC644937233-00000047/Plano de Recuperação e Resiliência, Portugal
- 02/C05-i01.01/2022.PC644937233-00000047/Plano de Recuperação e Resiliência, Portugal
- 02/C05-i01.01/2022.PC644937233-00000047/Plano de Recuperação e Resiliência, Portugal
- 02/C05-i01.01/2022.PC644937233-00000047/Plano de Recuperação e Resiliência, Portugal
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

