Survey on Alopecia Areata Patients' Reported Factors that Determine Severity of Alopecia Areata: A Nationwide Multicenter Study
- PMID: 39623614
- PMCID: PMC11621644
- DOI: 10.5021/ad.24.033
Survey on Alopecia Areata Patients' Reported Factors that Determine Severity of Alopecia Areata: A Nationwide Multicenter Study
Abstract
Background: Alopecia areata (AA) is characterized by hair loss on the scalp and body, significantly impacting patients' quality of life based on its severity.
Objective: This study aims to identify crucial factors influencing the perception of severe AA from the patients' viewpoint.
Methods: A web-based survey was conducted among AA patients attending dermatology departments at 21 university hospitals in Korea. The survey comprised 17 criteria, exploring both clinical characteristics of AA patients and subjective determinants of disease severity.
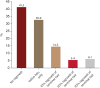
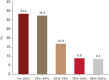
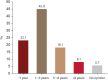
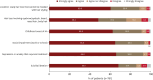
Results: A total of 791 AA patients and their caregivers participated in the survey. Approximately 30% of respondents developed AA during childhood, with 43.5% experiencing chronic courses lasting over 3 years. Half of the participants exhibited more than 20% scalp hair loss, and 42% reported additional hair loss on other body parts, such as eyelashes and nose hair. Most respondents agreed that patients with ≥20% scalp hair loss should be categorized as having severe AA. They also identified longer disease duration, involvement of non-scalp body hair, treatment refractoriness, and social or mental impairment requiring medical intervention as factors indicating increased disease severity.
Conclusion: This survey underscores the significant impact of AA on patients' quality of life and highlights existing unmet needs in current treatment modalities.
Keywords: Alopecia areata; Needs Assessment; Severity of Illness Index; Surveys and Questionnaires; patients.
© 2024 The Korean Dermatological Association and The Korean Society for Investigative Dermatology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Smith A, Trüeb RM, Theiler M, Hauser V, Weibel L. High relapse rates despite early intervention with intravenous methylprednisolone pulse therapy for severe childhood alopecia areata. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:481–487. - PubMed
-
- Strazzulla LC, Wang EH, Avila L, Lo Sicco K, Brinster N, Christiano AM, et al. Alopecia areata: disease characteristics, clinical evaluation, and new perspectives on pathogenesis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Chiang KS, Mesinkovska NA, Piliang MP, Bergfeld WF. Clinical efficacy of diphenylcyclopropenone in alopecia areata: retrospective data analysis of 50 patients. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2015;17:50–55. - PubMed
-
- Phan K, Ramachandran V, Sebaratnam DF. Methotrexate for alopecia areata: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:120–127.e2. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

