School-based hearing screening of first-grade students in Saudi Arabia: A pilot study
- PMID: 39625087
- PMCID: PMC11622043
- DOI: 10.4102/sajcd.v71i1.1063
School-based hearing screening of first-grade students in Saudi Arabia: A pilot study
Abstract
Background: Hearing loss in children is a global concern. Early identification and intervention are critical for minimising the adverse effects of hearing loss. Despite the implementation of hearing screening programmes in Saudi Arabia, more research is needed on the audiological profiles of first-grade students.
Objectives: This study aimed to characterize the audiological profile of first-grade students in Saudi Arabia and to raise awareness among parents, schools, and decision-makers about the need for hearing screening programs and the implementation of an effective monitoring and management system in the country.
Method: This cross-sectional descriptive study assessed the audiological profile of 308 first-grade students in Riyadh, the capital of Saudi Arabia, using pure-tone audiometry (PTA) and tympanometry. Additionally, two questionnaire-based assessments, one for parents and one for the home teacher, were developed to predict students who failed PTA.
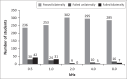
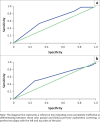
Results: Among the students screened, 26.3% failed PTA. Tympanometry identified abnormal middle ear function in 30.5% of the students. The discrimination capacity of both questionnaires in identifying students who failed PTA screening was poor.
Conclusion: A 26.3% prevalence rate of PTA screening failure, and a 30.5% of middle ear pathologies were noted. Both parent and teacher questionnaires were ineffective tools for identifying hearing loss among first-grade children who failed PTA screening.Contribution: This pilot study recommends that primary schools incorporate hearing screening as a regular practice of their preventative healthcare system. The study emphasises the importance of establishing international standards for school-based hearing screening to enhance its efficacy and develop more effective hearing screening questionnaires.
Keywords: Saudi Arabia; children; hearing loss; pure-tone audiometry; school health service; screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no financial or personal relationships that may have inappropriately influenced them in writing this article.
Figures
References
-
- Al Daajani, M.M., Al-Habib, D.M., Ibrahim, M.H., Al Shewear, N.A., Fagihi, Y.M., Alzaher, A.A., Alfaleh, A.F., & Alabdulkareem, K.I. (2019). Prevalence of health problems targeted by the national school-based screening program among primary school students in Saudi Arabia. Healthcare (Basel), 9(10), 1310. 10.3390/healthcare9101310 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- American Academy of Audiology . (2011). Childhood hearing screening guidelines. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/hearingloss/documents/aaa_childhood-hearing-g...
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources