Extracellular vesicles, RNA sequencing, and bioinformatic analyses: Challenges, solutions, and recommendations
- PMID: 39625409
- PMCID: PMC11613500
- DOI: 10.1002/jev2.70005
Extracellular vesicles, RNA sequencing, and bioinformatic analyses: Challenges, solutions, and recommendations
Abstract
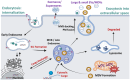
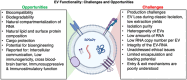
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are heterogeneous entities secreted by cells into their microenvironment and systemic circulation. Circulating EVs carry functional small RNAs and other molecular footprints from their cell of origin, and thus have evident applications in liquid biopsy, therapeutics, and intercellular communication. Yet, the complete transcriptomic landscape of EVs is poorly characterized due to critical limitations including variable protocols used for EV-RNA extraction, quality control, cDNA library preparation, sequencing technologies, and bioinformatic analyses. Consequently, there is a gap in knowledge and the need for a standardized approach in delineating EV-RNAs. Here, we address these gaps by describing the following points by (1) focusing on the large canopy of the EVs and particles (EVPs), which includes, but not limited to - exosomes and other large and small EVs, lipoproteins, exomeres/supermeres, mitochondrial-derived vesicles, RNA binding proteins, and cell-free DNA/RNA/proteins; (2) examining the potential functional roles and biogenesis of EVPs; (3) discussing various transcriptomic methods and technologies used in uncovering the cargoes of EVPs; (4) presenting a comprehensive list of RNA subtypes reported in EVPs; (5) describing different EV-RNA databases and resources specific to EV-RNA species; (6) reviewing established bioinformatics pipelines and novel strategies for reproducible EV transcriptomics analyses; (7) emphasizing the significant need for a gold standard approach in identifying EV-RNAs across studies; (8) and finally, we highlight current challenges, discuss possible solutions, and present recommendations for robust and reproducible analyses of EVP-associated small RNAs. Overall, we seek to provide clarity on the transcriptomics landscape, sequencing technologies, and bioinformatic analyses of EVP-RNAs. Detailed portrayal of the current state of EVP transcriptomics will lead to a better understanding of how the RNA cargo of EVPs can be used in modern and targeted diagnostics and therapeutics. For the inclusion of different particles discussed in this article, we use the terms large/small EVs, non-vesicular extracellular particles (NVEPs), EPs and EVPs as defined in MISEV guidelines by the International Society of Extracellular Vesicles (ISEV).
Keywords: EVs; bioinformatics; extracellular vesicles; long‐read sequencing; short‐read sequencing; small RNA; transcriptomics.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Extracellular Vesicles published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Extracellular Vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
S.G. reports past consultancy or advisory roles for Taiho Pharmaceuticals; research funding from Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Genentech, EMD Serono, Pfizer and Takeda, unrelated to the current work. All other authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. N.D. and G.S. are awarded a patent entitled ‘Exosome vessels for delivery of molecular cargo’, US Patent 11,766,484.
Figures


References
-
- Abels, E. R. , Maas, S. L. N. , Nieland, L. , Wei, Z. , Cheah, P. S. , Tai, E. , Kolsteeg, C.‐J. , Dusoswa, S. A. , Ting, D. T. , Hickman, S. , El Khoury, J. , Krichevsky, A. M. , Broekman, M. L. D. , & Breakefield, X. O. (2019). Glioblastoma‐associated microglia reprogramming is mediated by functional transfer of extracellular MiR‐21. Cell Reports, 28(12), 3105–3119. 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.08.036 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NIH R21 AGO78848/Navneet Dogra
- U24 CA224319/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK124165/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK133885/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA224319/Sacha Gnjatic
- DK124165/Sacha Gnjatic
- NIH R01DK133885/Susmita Sahoo
- P20 CA264076/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Evox Therape/Susmita Sahoo
- NIHP20CA264076/S.O.H., M.D.S., E.T.
- NIH R01HL148786/Susmita Sahoo
- P30 CA196521/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- NIH P20CA264076/Navneet Dogra
- CA196521/Sacha Gnjatic
- R01 HL148786/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

