Feature selectivity and invariance in marsupial primary visual cortex
- PMID: 39625561
- PMCID: PMC11737535
- DOI: 10.1113/JP285757
Feature selectivity and invariance in marsupial primary visual cortex
Abstract
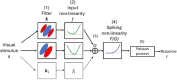
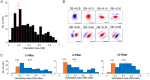
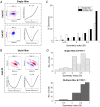
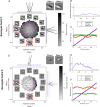
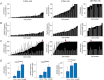
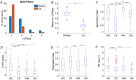
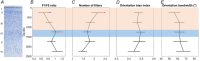
A fundamental question in sensory neuroscience revolves around how neurons represent complex visual stimuli. In mammalian primary visual cortex (V1), neurons decode intricate visual features to identify objects, with most being selective for edge orientation, but with half of those also developing invariance to edge position within their receptive fields. Position invariance allows cells to continue to code an edge even when it moves around. Combining feature selectivity and invariance is integral to successful object recognition. Considering the marsupial-eutherian divergence 160 million years ago, we explored whether feature selectivity and invariance was similar in marsupials and eutherians. We recovered the spatial filters and non-linear processing characteristics of the receptive fields of neurons in wallaby V1 and compared them with previous results from cat cortex. We stimulated the neurons in V1 with white Gaussian noise and analysed responses using the non-linear input model. Wallabies exhibit the same high percentage of orientation selective neurons as cats. However, in wallabies we observed a notably higher prevalence of neurons with three or more filters compared to cats. We show that having three or more filters substantially increases phase invariance in the V1s of both species, but that wallaby V1 accentuates this feature, suggesting that the species condenses more processing into the earliest cortical stage. These findings suggest that evolution has led to more than one solution to the problem of creating complex visual processing strategies. KEY POINTS: Previous studies have shown that the primary visual cortex (V1) in mammals is essential for processing complex visual stimuli, with neurons displaying selectivity for edge orientation and position. This research explores whether the visual processing mechanisms in marsupials, such as wallabies, are similar to those in eutherian mammals (e.g. cats). The study found that wallabies have a higher prevalence of neurons with multiple spatial filters in V1, indicating more complex visual processing. Using a non-linear input model, we demonstrated that neurons with three or more filters increase phase invariance. These findings suggest that marsupials and eutherian mammals have evolved similar strategies for visual processing, but marsupials have condensed more capacity to build phase invariance into the first step in the cortical pathway.
Keywords: brain evolution; marsupial; neuroscience; receptive field; visual cortex.
© 2024 The Author(s). The Journal of Physiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Adelson, E. H. , & Bergen, J. R. (1985). Spatiotemporal energy models for the perception of motion. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, Optics and Image Science, 2(2), 284–99. - PubMed
-
- Almasi, A. , Meffin, H. , Cloherty, S. L. , Wong, Y. , Yunzab, M. , & Ibbotson, M. R. (2020). Mechanisms of feature selectivity and invariance in primary visual cortex. Cerebral Cortex, 30(9), 5067–5087. - PubMed
-
- Azevedo, F. A. , Carvalho, L. R. , Grinberg, L. T. , Farfel, J. M. , Ferretti, R. E. , Leite, R. E. , Filho, W. J. , Lent, R. , & Herculano‐Houzel, S. (2009). Equal numbers of neuronal and nonneuronal cells make the human brain an isometrically scaled‐up primate brain. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 513(5), 532–541. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
