Repurposing of lonafarnib as a treatment for SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 39625789
- PMCID: PMC11721293
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.182704
Repurposing of lonafarnib as a treatment for SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
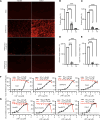
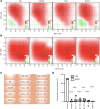
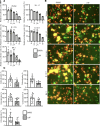
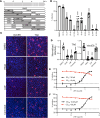
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), has emerged as a global pandemic pathogen with high mortality. While treatments have been developed to reduce morbidity and mortality of COVID-19, more antivirals with broad-spectrum activities are still needed. Here, we identified lonafarnib (LNF), a Food and Drug Administration-approved inhibitor of cellular farnesyltransferase (FTase), as an effective anti-SARS-CoV-2 agent. LNF inhibited SARS-CoV-2 infection and acted synergistically with known anti-SARS antivirals. LNF was equally active against diverse SARS-CoV-2 variants. Mechanistic studies suggested that LNF targeted multiple steps of the viral life cycle. Using other structurally diverse FTase inhibitors and a LNF-resistant FTase mutant, we demonstrated a key role of FTase in the SARS-CoV-2 life cycle. To demonstrate in vivo efficacy, we infected SARS-CoV-2-susceptible humanized mice expressing human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and treated them with LNF. LNF at a clinically relevant dose suppressed the viral titer in the respiratory tract and improved pulmonary pathology and clinical parameters. Our study demonstrated that LNF, an approved oral drug with excellent human safety data, is a promising antiviral against SARS-CoV-2 that warrants further clinical assessment for treatment of COVID-19 and potentially other viral infections.
Keywords: COVID-19; Drug screens; Drug therapy; Molecular biology; Virology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Multidisciplinary Approaches Identify Compounds that Bind to Human ACE2 or SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein as Candidates to Block SARS-CoV-2-ACE2 Receptor Interactions.mBio. 2021 Mar 30;12(2):e03681-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03681-20. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33785634 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and Evaluation of Entry Inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 and Its Emerging Variants.J Virol. 2021 Nov 23;95(24):e0143721. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01437-21. Epub 2021 Sep 22. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34550770 Free PMC article.
-
Stenoparib, an Inhibitor of Cellular Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase, Blocks Replication of the SARS-CoV-2 and HCoV-NL63 Human Coronaviruses In Vitro.mBio. 2021 Jan 19;12(1):e03495-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03495-20. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33468703 Free PMC article.
-
The Repurposed ACE2 Inhibitors: SARS-CoV-2 Entry Blockers of Covid-19.Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2021 Oct 8;379(6):40. doi: 10.1007/s41061-021-00353-7. Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2021. PMID: 34623536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contributions of human ACE2 and TMPRSS2 in determining host-pathogen interaction of COVID-19.J Genet. 2021;100(1):12. doi: 10.1007/s12041-021-01262-w. J Genet. 2021. PMID: 33707363 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

