Early assessment of antibodies decline in Chagas patients following treatment using a serological multiplex immunoassay
- PMID: 39627222
- PMCID: PMC11615370
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-54910-x
Early assessment of antibodies decline in Chagas patients following treatment using a serological multiplex immunoassay
Abstract
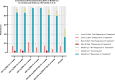
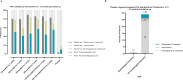
Chagas disease following infection with Trypanosoma cruzi is a major public health issue, with the disease spreading beyond endemic regions and becoming more global due to the migration of infected individuals. The currently available anti-parasitic drugs, nifurtimox and benznidazole, remain insufficiently evaluated for their efficacy in adult patients. A key challenge is the lack of markers for parasitological cure, which also precludes the development of new treatments. Consequently, there is a critical need for a practical method to assess drug performance within a short timeframe. In this retrospective analysis of the phase 2 randomized controlled BENDITA trial (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT03378661), we report the potential of a serological multiplex method (MultiCruzi), combined with advanced statistical analytical methods, to measure the response to anti-parasitic treatment of adult Chagas patients. Applying this approach to serum samples from adult patients in the indeterminate chronic stage of Chagas disease, treated with different benznidazole regimens and combinations, we predict treatment efficacy after just 6 months of follow-up, in sharp contrast to data obtained with conventional and recombinant T. cruzi ELISA tests. The obtained results are also compared with the PCR data. We propose integrating MultiCruzi as a serological method endpoint in proof-of-concept clinical trials for Chagas disease.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: U.S. and M.Z. are employed by InfYnity Biomarkers. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

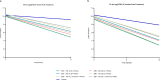
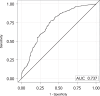
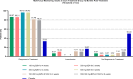
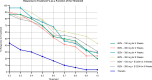
References
-
- Pérez-Molina, J. A. & Molina, I. Chagas disease. Lancet391, 82–94 (2018). - PubMed
-
- WHO. Chagas Disease.https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/chagas-disease-(america... (2023).
-
- Rassi, A., Rassi, A. & Marcondes de Rezende, J. American trypanosomiasis (Chagas Disease). Infectious Disease Clinics of North America26, 275–291 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Nunes, M. C. P. et al. Chagas cardiomyopathy: an update of current clinical knowledge and management: a scientific statement from the American heart association. Circulation138, e169–e209 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

