Functional expression and regulation of eukaryotic cytochrome P450 enzymes in surrogate microbial cell factories
- PMID: 39628612
- PMCID: PMC11610987
- DOI: 10.1016/j.engmic.2022.100011
Functional expression and regulation of eukaryotic cytochrome P450 enzymes in surrogate microbial cell factories
Abstract
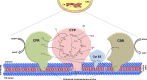
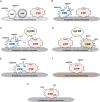
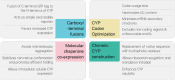
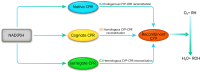
Cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes play crucial roles during the evolution and diversification of ancestral monocellular eukaryotes into multicellular eukaryotic organisms due to their essential functionalities including catalysis of housekeeping biochemical reactions, synthesis of diverse metabolites, detoxification of xenobiotics, and contribution to environmental adaptation. Eukaryotic CYPs with versatile functionalities are undeniably regarded as promising biocatalysts with great potential for biotechnological, pharmaceutical and chemical industry applications. Nevertheless, the modes of action and the challenges associated with these membrane-bound proteins have hampered the effective utilization of eukaryotic CYPs in a broader range. This review is focused on comprehensive and consolidated approaches to address the core challenges in heterologous expression of membrane-bound eukaryotic CYPs in different surrogate microbial cell factories, aiming to provide key insights for better studies and applications of diverse eukaryotic CYPs in the future. We also highlight the functional significance of the previously underrated cytochrome P450 reductases (CPRs) and provide a rational justification on the progression of CPR from auxiliary redox partner to function modulator in CYP catalysis.
Keywords: Cytochrome P450 enzymes; Cytochrome P450 reductase; Electron transfer; Heterologous expression; Membrane-bound proteins; Microbial cell factories; N-terminal transmembrane domain; Redox partners.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of Shandong University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Akhtar M., Wright J.N., Lee-Robichaud P. A review of mechanistic studies on aromatase (CYP19) and 17α-hydroxylase-17, 20-lyase (CYP17) J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011;125(1-2):2–12. - PubMed
-
- Alcaíno J., Fuentealba M., Cabrera R., et al. Modeling the interfacial interactions between CrtS and CrtR from Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous, a P450 system involved in astaxanthin production. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012;60(35):8640–8647. - PubMed
-
- Andersen, M.D., Møller, B.L. Use of methylotropic yeast Pichia pastoris for expression of cytochromes P450. Methods Enzymol. 2002;357:333-42. doi:10.1016/s0076-6879(02)57691-6. PMID:12424923. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

