A comparative study on the genomes, transcriptomes, and metabolic properties of Escherichia coli strains Nissle 1917, BL21(DE3), and MG1655
- PMID: 39628614
- PMCID: PMC11610980
- DOI: 10.1016/j.engmic.2022.100012
A comparative study on the genomes, transcriptomes, and metabolic properties of Escherichia coli strains Nissle 1917, BL21(DE3), and MG1655
Abstract
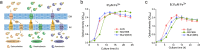
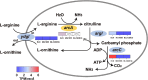
Escherichia coli is the most well-studied model prokaryote and has become an indispensable host for the biotechnological production of proteins and biochemicals. In particular, the probiotic status of one E. coli strain, E. coli Nissle 1917 (EcN) has helped it become a new favorite amongst synthetic biologists. To broaden its potential applications, here we assemble a comparative study on the genomes, transcriptomes, and metabolic properties of E. coli strains EcN, BL21(DE3), and MG1655. Comparative genomics data suggests that EcN possesses 1404 unique CDSs. In particular, EcN has additional iron transport systems which endow EcN with a higher tolerance to iron scarcity when compared to two other E. coli strains. EcN transcriptome data demonstrates that E. coli strains EcN, BL21(DE3), and MG1655 all have comparable activities of the central metabolic pathway, however only EcN inherits the arginine deiminase pathway. Additionally, we found that EcN displayed a lower expression of ribosomal proteins compared to BL21(DE3) and MG1655. This comparative study on E. coli strains EcN, BL21(DE3), and MG1655 aims to provide a reference for further engineering EcN as a biotechnological tool.
Keywords: Escherichia coli Nissle 1917; comparative genomics; probiotics; synthetic biology; transcriptome.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Benesty J, Chen J, Huang Y, Cohen I. Springer Topics in Signal Processing; 2009. Pearson correlation coefficient. Noise Reduction in Speech Processing; pp. 1–4.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

